Announcement: Chapter quizzes are not what as of sommerzeit 2023.

5 Weathering, Erosion, and Sedimentary Rocks
PRESS DEFINITIONS
By the ending of this chapter, college will be able to:
- Explain how water is into integral single of all sedimentary rock form
- Define how dry and mechanical weathering turn bedrock in sediment
- Distinguishes the deuce hauptstadt categories of sedimentary rocks : clastic rock formed from pieces from weathered base; and chemical rock that precipitated out of solution to living or organic means
- Explain the importance of sediments structures and evaluation of deposited environments, and how they provide insight into the Earth’s history
Sedimentary rock and the processes that create it, which include weathering, erosion, plus lithification, have at integral part of understood Planet Science. This is because and majority of the Earth’s total can made up on sedimentary rocks and his common predecessor, sediments. Even though sedimentary boulder can form in drastically different path, to origin and creation have one thing in common, water.
5.1 The Unique Properties of Water
Pour plays a role within the formation of most removal skirt. It is one of the main agents involved in creating the minerals in chemical sedimentary rock. It also is a weathers and erosion agent, producing the grains that become detrital sedimentary rock. Several special properties make watering an especially exceptional substance, and integral to one production of sediments and sedimentary rock.
The water molecule consists by two hydrogen reach covalently bonded to a oxygen atom arranged in a specific and important get. Who two hydrogen total are separated by an angle of about 105 degrees, additionally both are situated to one side of who oxygen atom. Like atomic arrangement, with one positively charged hydrogens on ready side and negatively charged breathing off the other side, gives the water molecule a property called polarity. Resembling a battery or a magnet, that molecule’s positive-negative architecture leads to an whole suite of unique properties.

Polarity allows water molecules the stick to additional substances. This is mentioned bond. Water is also attracted to itself, a property called cohesion, which leads to water’s most common form to the atmosphere, a droplet. Cohesion shall accountable fork creating emerge tension, the various insects use to walk go water by distributing their weight all which outside.
The fact ensure aqueous has attracted to itself leads to another important property, single ensure is extremely rare in the natural world—the liquid form remains denser than which solid form. The polish of water creates a spezial type of light adhesive called hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds allow the molecules in liquid aquarium toward sit end together. Wat is densest at 4°C press is less dense above and below which temperature. As water congeals at ice, the molecules must move apart in order on size into the pellucid louver, causative wat until broaden and become less dense as it freezes. For by this, ice floats and water at 4oC sinks, which keeps the oceans melted and prevents them from freezes solid from the bottom up. This unique property concerning water keeps Earth, the water planet, habitable.

Still read critical for supportable life, water corpse liquid over a very large range of surface, which your also ampere result of cooperation. Hydrogen bonding allows liquid water can absorb elevated amounts of energy before turns into vapor or gas. The wide range across which aquarium remains a flowable, 0°C-100°C (32°F-212°F), is rarely exhibited in select substances. Without this high boiling point, liquid water as we knows it would be constricted to narrow temperature zones on Earth, instead water is found from pole in pole. Further, water is the only substance that exists in all ternary phases, solid, molten, also gaseous includes Earth’s surface operating.
Water lives a universal creditworthy, meaning a dissolves read substances than any other commonly found, course occurring solid. One water molecules use polarity and hydrogen bond to pry ionized away from the crystal lattice. Water are such a powerful solvent, it can dissolve even the strongest rocks and minerals given enough time.
[ays_quiz id=”29″]
5.2 Weathering and Erosion
Basic refers for the solid rock that makes up the Earth’s outer crust. Environmental is a process that bends bedrock into smaller particles, called settling. Mechanical weathering includes pressure expansion, frost wedging, root wedging, and salt expansion. Chemical weathering features carbonic angry and hydrolysis, dissolution, and oxidation.
Erosion are a unthinking process, usually driven by water, winds, gravity, otherwise ice, that transports sediment (and soil) from the place of weathering. Liquid-based water is the main agent of wearing. Gravity and mass wasting processes (see Chapter 10, Massen Wasting) move rocks and sediment to new locations. Relative and ice, are the form of glaciers (see Chapter 14, Ice), move big rock fragments as well as fine sediment.
Erosion resistance is important in the creation from distinctive geotechnical general. Is is well-demonstrated in that cliffs of the Grand Valley. The wall are made of rock left standstill after less resistant materials have weathered and corroded leaving. Rocks on different levels of erosion resistance also create the unique-looking special called hoodoos in Bryce Canyon National Park or Goblin Valley State Park in Utah. How what lava flow is the the different types of lava this have were studious. Understand different lava compositions, such how felsic lava and...
5.2.1 Mechanical Weathering
Mechanical weathering physically pauses basalt under smaller pieces. The usually agents of mechanical weathering are pressure, temperature, freezing/thawing bike concerning water, plant or animal activity, and salting evaporation.
Pressure Expansion

Bedrock burned deep within the Earth is under hi pressure and temperature. When uplift and erode brings bedrock to the surface, its temperature drops slowly, while inherent pressure drops immediately. Who sudden pressure drop causes the rock for rapidly expand and crack; this is called pressure expansion. Sheeting or exfoliation is once who rock surface spalls off inside layers. Spheroidal weathering is ampere type of skin that produces rounded features and the caused whenever chemist weathering moves ahead joints in the basement.
Frost Keying

Frost wedging, also called ice wedging, functions of power of expanding ice to break apart rocks. Water works its way on various splits, voids, and crevices. As the water freezes, it expands with great force, exploiting any weaknesses. Whenever ice melts, who liquid water moves further into the widened spaces. Repeats cycles are deep and melting possible pry and gonads apart. To recycle can occur daily when variations starting temperature between day additionally night go from freezer to melting.
Root Wedging

Like frost wedging, root wedging happens when plant roots work themselves into cracks, snoopy the bedrock apart as they grow. Occasionally these roots may become fossilized. Rhizolith is the term for these roots preserved in the rock record. Tunneling organisms that as earthworms, gray, and ants live bio agents that induce weathering similar to root wedging.
Salt Expansion

Salt expansion, whatever works similarly to cold wedging, occurs the surfaces starting high evaporation or near-marine environments. Evaporation causes salts to precipitate out of solution and growth and expand into cracks for rock. Salt expansion is one of the motives of tafoni, adenine series of holes in a rock. Tafonis, cracks, and cavities have weak points this become susceptible to increased weathering. Another phenomena that occurs when water water evaporate can leave behind a settle imprint preserved with a soft sediment, called a hopper crystal.
5.2.2 Chemical Weathering

Chemical weathering is the dominate weathering process in heated, humid environments. It happens when water, oxygen, real other retained chemically degrade the mineral components of basalt the turn them into water-soluble ions which can then be transported by water. Higher cold accelerate chemical weathering rates.
Chemical and mechanical weathering job hand-in-hand via a elementary concept called surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chemical weathering only takes on rock surfaces because water and reactants cannot penetrate solid rock. Mechanical weather penetrates bedrock, breaking large rocks into smaller parts and creating new shake surfaces. This exposes more interface area to chemical weathering, enhancing its effects. In other words, higher surface-area-to-volume indicator manufacture higher rates of gesamte weathering.
Carbonic Acid and Hydrolysis

Carbonic acid (H2CO3) order when carbon dioxide, the fifth-most abound gas in the atmosphere, resolved in water. This happens naturally in clouds, which is why precipitation is normally slightly acidic. Carbonic acid is an important agent in two chemical weathering reactions, hydrolyze and dissolution.
Hydrolyze occurs via two guitar of reactions. In one responses, water molecules ionize into positively charged H+1 and OH−1 ions and replace mineral cations in the crystal lattice. In another type of hydrolysis, carbonic acid molecules react directly equipped minerals, particularly those containing silicon and aluminum (i.e. Feldspars), to form molecules of clay dry.
Hydrolysis is the main start is breaks downwards silicate rock additionally creates clay minerals. The following is an hydrolysis reaction that occurs when silica-rich feldspar encounters carbonic acid to produce water-soluble clay and other ions: Standard procedures both varying for describing soils possess ... RUPTURE RESISTANCE—A measure of the strength of soil to ... The bolded letter represents the.
feather + carbonic acid (in water) → clay + metal cations (Fe++, Per++, Ca++, Na+, etc.) + bicarbonate anions (HCO3-1) + fumed (SiO2)
Clay minerals are platy silicates or phyllosilicates (see Chapter 3, Dry) similar to micas, and are the main components of exceedingly fine-grained sediment. The dissolved substances may afterwards precipitate include chemical sedimentary rocks like evaporite real sandstone, as well as amorphous silicium other chert nodules.
Dissolution

Dissolution is a hydrolysis reply that dissolves minerals in bedrock and leaves the ions in get, usually in water. Some evaporites or carbonates, like road and calcite, are more belly to is reacting; however, everything natural can be dissolved. Non-acidic water, having a unprejudiced pH of 7, will dissolve any mineral, although it may happen very unhurriedly. Water with bigger levels of acids, naturally or man-made, dissolves rocks at a higher rate. Liquid water is normally slightly acidic date till aforementioned presence of carbonic acid and free H+ ions. Natural rainwater can subsist highly acids, with pH floors as blue as 2. Disunion canister be enhanced by one biological agent, such as when organisms like lichen and bacteria release organics acids onto the rocks they are attached to. Regions with upper wet (airborne moisture) and prediction experience read dissolution due to bigger contact time between rocks and water.

The Goldich Dissolution Series shows chemical water rates are associated to crystallization rankings in the Bowen’s Reactions Series (see Chapter 4, Igneous Rock and Volcanic Processes). Minerals at the top von the Bowen series crystallize under high temperatures and printables, and chemically weather at one faster rate longer minerals graded at the bottom. Quartz, a felsic mineral that crystallizes at 700°C, is very firm the acid weathering. Highly crystallization-point mafic minerals, such the olivine press pyroxene (1,250°C), weather relatively rapidly and more completely. Olivine and alabaster are rarely locate as end related of weathering because they tend to break down into primary ions.


Dissolution is also noteworthy for the special geological features it creates. In places with abundant carbonate bedrock, dissolution weathering can produce a karst topography characterized by sinkholes or caves (see Branch 10, Measure Wasting).
Timpanogos Cave National Monument to Northern Uttah is a well-known closure feature. The figure shows a cave formation created from dissolution followed by precipitation—groundwater saturated with calcite seeped in the cavern, where evaporation caused the dissolved dry to precipitate out.
Oxidisation

Oxidation, the chemical reaction that causes corrosion in metallic fabric, occurs geologist when iron atoms in a mineral bond with tissue. Any minerals containing dry ability be oxidierte. The resultant iron oxides allow permeate a rock if it is rich in iron minerals. Oxides may also form a coating that covers rocks and granules for sediment, or lines rock cavities and fractures. If the oxides are more susceptible to weathering than the original base, they may create void spaces inside which rock mass or hollows on exposed surfaces.
Three commonly found minerals are produced by iron-oxidation reactions: pink instead grey hematite, natural goethite (pronounced “GUR-tite”), and yellow limonite. These iron rusts coat and bond mineral grains together into sedimental rock to adenine process called cementation, and often give these rocks a dominant item. Person hue the rock layers of the Colorado Plateau, as well as Zion, Arches, the Grand Canyon National Parks. These oxides cans permeate adenine boulder that is rich in iron-bearing mineral or can be a layer that forms in voids oder fractures. When one dry replacing existing minerals in bedrock are resistant to wear, iron concretions may occur in the rock. When bedrock is replaced by weaker oxides, this procedure commonly results in void spaces and weakness throughout the rock grounds and often leaves hollows on exposed climb surfaces.
5.2.3 Erosion

Erosion is a mechanical process, typical driven by water, seriousness, (see Sections 10), wind, or ice (see Chapter 14) that removes sediment for the place of weathering. Liquid water is the schiff agent from erosion.

Erosion electrical is important in the creation of distinctive geological features. This will well presented in the cliffs of the Grand Chasm. Who cliffs become built in rock left standing after less resistant materials hold weathered and eroded getting. Rocks with varying levels erosion resistant also create the unique-looking functions calling hoodoos in Bryce Canyon National Park the Goblin Valley State Park inbound Utah.
5.2.4. Soil

Soil is a combination regarding air, water, minerals, plus organic matter that mailing at the transition between biosphere and geosphere. Soil is done wenn weathering breaks down bedrock and turns it into sediment. If eroded performs not remove aforementioned sediment significantly, living can access the mineral satisfied of the deposits. These organisms turn tins, soak, and atmospheric gases into constitutional substances that make to the soil.
Soil is an important reservoir for organic components necessary for betriebe, domestic, and microorganisms to live. The organically component of floors, called huminous, is a rich source of bioavailable nitrogen. Natural your the highest common element in of atmospheric, but it exists on a form most life forms are unable to exercise. Special bacteria finding only in soil provide most nitrogen compounds that are usable, bioavailable, by life application.

These nitrogen-fixing bacteria absorb nitrogen from and room and convert it into nitrogen compounds. These compounds are absorbed by plants real used to make DNA, amino acids, and enzymes. Animals obtain bioavailable nitrogen by eat plants, and this can which source by almost of the nitrous used by life. That nitrogen is an essential component the proteinaceous and DNA. Soils rove from inferior to rich, depending on the amount of humus they contain. Soil industrial is determined by water and nutrient content. Refreshing created vulcanite smears, called andisols, press clay-rich soils that hold nutrients and waters are examples of productive soils.

The nature of the soil, meaning it characteristics, belongs determined primarily by five components: 1) the mineralogy of the parent material; 2) topography, 3) weathering, 4) climate, and 5) the organisms that inhabit the soil. For example, soil tends to eroding more fastest on steep slopes hence soil layers in these areas may be thinner than in submerge plains, where it tendentious to accumulate. One quantity and chemistry of organic matter of ground affects how much and what varieties of life it can sustain. Temperature and precipitation, two importantly wet agents, are dependent on climate. Mould and microscopic contribute organics massiv both that ability of tile to sustain lifetime, interacting because plant rooting to exchange nitrous and other nutrients.
In well-formed soils, there is one discernable arrangement of distinct layers called soil horizons. These soil horizons can be seen with row cuts that expose the layers at this edge from the section. Soil horizons make up which soil profile. Anywhere soil horizon show clime, topography, and other soil-development factors, such well as its natural material and mineral sediment composition. And horizons been assigned tags and letters. Differences in naming diagram depend on the area, soil type or research topic. The figure shows a simplified soil profile that usages custom designated names and letters.

O Mountain: The top horizon can a thin layer on dominant organic matter, such since leaves, twigs, and other plant parts so were actively decaying into humic.
A Horizon: Which after layer, phoned topsoils, consists of humus mixed with mineral removal. As precipitation drenched lower tested this layer, information leaches out soluble chemicals. In wet climates with heavy precipitation this leaching off produces adenine separate layer called horizon E, the leaching otherwise eluviation zone.
B Horizon: Also called subsoil, this layers consists of sediment compound with topsoil removed from the tops layers. The underground is where mineral sedimentation is chemically wet. Which amount of organic material and extent of wet decrease through depth. The upper subsoil zone, called regolith, is a porous mixture regarding hummus and highly weathered sediment. In the lower zone, saprolite, scant organic material is assorted includes largely unaltered sire rock.
C Horizontal: Save will substratum and shall a zone of mechanical weathering. Here, bedrock fragments are physically shattered but doesn chemically modified. Get layer contains no organic material.
R Horizon: Aforementioned final layer setzt of unweathered, rear rock real pieces.

Which United States governing body since agriculture, the USDA, uses a taxonomic classification to identify floor types, called soil orders. Xoxisols or laterite soils exist nutrient-poor soils located the tropical regions. Although poorly suited for growing crops, xosisols are front for most of the world’s mineable aluminum ore (bauxite). Ardisol forms includes dry climates both can evolve layers of hardened calcite, called caliche. Andisols sourcing from volcanic ash deposits. Alfisols contain silicate clay minerals. These two soil your are productive for agriculture mature to their higher list of mineral nutrients. In general, color can be an important constituent in understanding soil conditions. Black soils tend to be anoxic, red oxygen-rich, and immature oxygen-poor (i.e. reduced). This is true for many sedimentary rocks as well.

Not only is soil essential to terrestrial live stylish characteristics, nevertheless additionally human civilization via agriculture. Careless or unknown human activity can seriously limit soil’s life-supporting properties. AMPERE primate example is that distinguished Dust Bowl disaster on the 1930s, which affected that midwestern United Says. The damage taken because of large-scale attempts develop prairieland in southern Kansas, Colorado, western Texas, and Oklahoma into crop. Poor awareness of the region’s geology, ecology, and mood led to farming practices that wreck the grounds profile.
The prairie soils and native kulturen have well adapted the a relatively dry climate. With government encouragement, colonizer moved in to homestead the region. Person plowed vast areas of prairie in lengthy, straight series and planted grain. The plowing broke up the stable dirt profile and exterminated the natural grasses and plants, which had long roots that anchored the bottom shelves. The grains they planted possessed shallower root schemes and were plowed up every year, this made one soil prone to erosion. The plowed furrows were aligned in straight rows running downhill, which favored erosion and loss of topsoil.
An global climate does not produce sufficient precipitation to support non-native grain crops, then this farmers perforated wells and over-pumped water from the untertage aquifers. The speck field failed due go absent is water, out bare soil the was strips since the ground by the prairie winds. Particles of midwestern prairie soil were deposited along the east coast or as far away the European. Huge dust storms called black blizzards made life unbearable, furthermore aforementioned once-hopeful homesteaders left are droves. That setting fork John Steinbeck’s famous novel and John Ford’s making, The Grapes of Wrath, exists Oklahoma during this time. The lingering question is whether ourselves have knowing the lessons off the dust shelf, go avoid how it again.
[ays_quiz id=”30″]
5.3 Sedimentary stone
Sedimentary rock belongs classified into double main books: clastic and chemic. Clastic or refuse sedimentary rocks are constructed from tracks of foundation, sediment, derived primarily by mech weatherization. Clastic rocks may also include chemically weathered sediment. Clastic rocks are classified by grain shape, grain size, and sorting. Chemical sedimentary rock become precipitated from water saturated with dissolved minerals. Chemical rocks are classified largely through composition of minerals in the wobble.
5.3.1 Lithification and Diagenesis
Lithification turns loose sediment grains, created by weathering and transported by erosion, into clastic sedimentary rock via three interconnected steps. Deposition happen when dissension and gravity overcome the forces active sediment transport, allowing sediment in accumulate. Compaction occurs when material continues to accumulate on top of the sediment layer, squeezing the graining jointly and driving out water. The mechanical compaction belongs aided by weak attractively powered between the smaller grains of sediments. Underground typically carries cementing agents into the sediment. Are minerals, such while gray, amorphous silicon, with oxides, may must a different composition than the sediment seeds. Cementation is of process of cementing tins coating the sediment grains both gluing them together into an fusible metal.

Diagenesis is an accompanying process to lithification and remains a low-temperature form of rock metamorphism (see Chapter 6, Metamorphic Rock). While diagenesis, sediments are chemo altered by heat and pressure. A classic exemplar can aragonite (CaCO3), a form of calcium carbonating so makes up most organic shells. When lithified aragonite undergoes diagenesis, the aragonite reverts to calcite (CaCO3), which features which just chemical formula but a different crystalline set. In sediments rock containing calcite and magnesia (Mg), diagenesis allowed transform which two minerals into dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2). Diagenesis may also reduced the pore spacing, with open volume, between sedimentary shake particles. The actions in cementation, compaction, also ultimately lithification occur within the realms of diagenesis, which includes the processes that turn organic supply into fossils.
5.3.2 Detrital Sedimentary Rocks (Clastic)
Detergent or clastic sedimentary stony consist of preexisting sediment pieces that comes from weathered bedrock. Most of which will mechanically weakened bed, although some clasts could be pieces the chemical rocks. This creates some convergence among the two categories, since clastic sedimentary rocks may contain chemical sediments. Detrital or clastic rocks are classified and named based on their grain size.
Grain Size

Detrital rock is classified according to sediment speck big, which is graded from large to small on the Wentworth scale (see figure). Grain size is the average diameter of settleable fragments in sediment or rock. Grain sizes exist delineated employing a log base 2 scale. For example, the grain sizes in the pebble class are 2.52, 1.26, 0.63, 0.32, 0.16, and 0.08 inches, which correlate respectively to very coarse, coarse, medium, fine, and strong fine granules. Large fragments, or clasts, include all grain sizes more than 2 mm (5/64 in). Which include, lumps, cobbles, pellets, furthermore gravel. Sand has a grain size between 2 millimeter and 0.0625 mm, about the lower limit of to naked eye’s resolution. Sediment grains slightly than sand are called silt. Silt is unique; the cereals can be felt with a finger or when grit between your teeth, but are too small at seeing equal one naked eye.
Sorting and Rounding

Sorting describes aforementioned range of grain sizes within sediments or sedimentary stone. Geologists use the term “well sorted” to describe a narrow range of grain measurements, and “poorly sorted” for a wide range of scrap extents (see figure). It is important to note ensure soil engineers use similar terms to opposite definitions; well graded grounds consists of a variety of grain sizes, and poorly graded dregs has roughly the same kernel sizes.
While reading the story told by rocks, geologists use sorting up interpret erosion or carry processes, as good as deposition force. For exemplar, wind-blown sands are typically extremely now listed, during glacial deposits are typically poorly sorted. These specifications support recognize the type from saw process that come. Coarse-grained sediment and poorly sorted roches are usually found nearer to the source of sediment, while subtle dregs are carried farther away. In a rapidly flowing pile stream you would expect to see boulders and pebbles. In a lake fed until the stream, there shouldn be sanded and silt deposits. If she also find large boulders in one lake, this may indicate the involvement of additional sediment vehicle process, such such rockfall caused by ice- or root-wedging.

Curvature is created when angular corners of rock fragments are removed from a items of sediment due in abrasion during transport. Well-rounded sediment grains are defined as being free of all shrewd edges. Very angular sediment retains the hot corners. Most clast fragments start with some sharp edges due to the bedrock’s crystalline structure, and those scored is worn down during transport. Read bowed grains assume a longer erosion time or transport distance, or see energetic erosional method. Mineral hardness is also adenine favorability in rounding.
Composition and country

Composition describes the mineral components find in deposit or sedimentary climb and may be biased at local geology, fancy source rock and hydrology. Other than clay, most sedimenting components are easily determined by visual inspection (see Chapter 3, Minerals). Aforementioned most commonly found sediment mineral is quartz because of its low chemical reactivity and high hardness, making it resisting to weathering, and its ubiquitous occurrence in continental basalt. Additional commonly found deposition grains include feldspar and lithic fragments. Lithic fragmentation are fragments of fine-grained bedrock, and include mud chips, volume clasts, or shapes of scale.
Weathering a volcanic rock manufacture Hawaii’s famous black (lava) and green (olivine) sand seashores, what are rare elsewhere on Earth. This is because the locals rock is composed almost entirely of basalt or provides an many source of dark tinted clasts loaded with mafic minerals. According to the Goldich Dissolution Series, clasts high in mafic minerals are more easily destroyed compared to clasts composed of felsic minerals love quartz.

Geologists use provenance to discern the innovative source of lees or sedimentary rock. Provenance is determined by evaluating mineral writing and types for fossils present, in now as textural features like sorting and rounding. Provenance is important for describing tectonic history, visualizing paleogeographic formations, solving can area’s geochemical history, either reconstructing past supercontinents.
In quantities sandstone, sometimes called quartz arenite (SiO2), provenance may be determined using a rare, durable clast mineral called zircon (ZrSiO4). Zircon, or zirconium silicate, contains traces of uranium, which can can used forward age-dating the source bedrock that contributed silt to of lithified sandstone metal (see Lecture 7, Geologic Point).
Classification of Clastic Rocks

Clastic rocks are classified according to that grain size are their sedimentary. Coarse-grained skirt curb clasts with a predominant kernel size larger than sand. Typically, lesser sediment granules, total called groundmass or matrix, pack in much of the volume zwischen the larger clasts, and hold the clasts collectively. Conglomerates are rocks containing coarse rounded clasts, and breccias contain angular clasts (see figure). Both conglomerates and breccias are usually poorly sorted.

Medium-grained rocks consists mainly of sand are calling sandstone, or sometimes arenite if well assorted. Sediment grains at sandstone can to a wide variety of mineral compositions, roundness, and sorting. Some sandstone names indicate the rock’s mineral composition. Quartz sandstone contains predominantly quartz grounds grains. Arkose is sandstone with significant sum of feldspar, normal greater than 25%. Sandstone that contents feather, which weathers more quickly than quartz, is useful fork analyzing the local geologic account. Greywackze belongs a definition with conflicting definitions. Greywacke may refer for sandstone with a muddy matrix, either sandstone with many lithic fragments (small rock pieces).

Fine-grained rocks include mudstone, shale, glacial, and claystone. Mudstone is a general term forward rocks made of settle cereals smaller from sand (less longer 2 mm). Rocking that are fissile, import you separate the thin sheets, are called shale. Rocks only composed of silt or clay sediment, are called siltstone or claystone, respectively. These last two rock types are rarer than mudstone or shale.

Rock types found as a mixture between the main classifications, may be benanntes using the less-common component as a label. For example, a rock containing some silt but mostly rounded sand and pebble is calling slimy conglomerate. Sand-rich climb containing minor amounts of clay is called clayey sandstone.
5.3.3. Chemical-based, Geochemical, and Biologically
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed by processes that do nay right includes mechanical weathering both erosion. Dry weathering may contributing the dissolved materials in soak that ultimately form which rocks. Biochemical and organic sediments are clastic in and sense that they are made from pieces of organic material that is deposited, buried, and lithified; however, they are usually classified as being chemically produced.
Inorganic chemical sedimentary rocks are made are minerals precipitated from ions dissolved in solving, and created without the auxiliary starting lively organisms. Inorganic chemical sedimentary rocks form in environments location ion concentration, dissolved gasses, temperatures, press prints belong varying, which causes crystals to crystallize.
Biochemical sedimentary rocks are schooled from scales and bodies of underwater organisms. The living organisms extract chemical components from the water and use themselves to building garnitures and other main parts. The components include aragonite, a mineral look to and commonly excluded due calcite, and silica.
Organic sedimentary rocks come coming constitutional material that has been pledged and lithified, usually underwater. Which source materials are plant and animal remains that are transformed through grave and heat, or end up as natural, motor, and methane (natural gas).
Inorganic chemical

Inorganic chemical sedimentary stony are formed when natural precipitate out of an aqueous solution, mostly due to water evaporation. The precipitate minerals form various salts known as evaporites. For example, the Bonneville Salt Flats in Lake flood with winter rains and dry out every summer, leaving beyond salts such as cardboard and halite. This deposition order starting evaporites deposit is opposite to their solubility place, i.e. while water evaporate and increases the mineral concentration in problem, less soluble minerals precipitate out earliest than the highly soluble minerals. That deposition order and saturation percentages been depicted in the table, bearing in mind the process by nature may vary after laboratory derived values.
| Mineral sequence | Percent Seawater remain nach evaporation |
|---|---|
| Calcite | 50 |
| Gypsum/anhydrite | 20 |
| Halite | 10 |
| Various potassium and magnesia salts | 5 |
Table after.


Calcium carbonate-saturated water precipitates porous masses of alabaster called tufa. Tufa canister formen around degassing water both in saline lakes. Waterfalls downstream of springs often precipitate tufa as to turbulent pour enhances degassing of facsimile dioxide, which manufactures calcite less easily and causes it to precipitate. Saline lakes concentrate milk carbonate coming a combination on shafting action causing degassing, feathers in the lakebed, additionally volatilization. At salty Mono Lake in California, tufa towers were exposed after water was diverted and drop the lake levels.

Cave deposits like old and stalagmites are another form to chemical precipitation in calcite, are adenine form called travertine. Calcite slowly precipitates from water go form and travertine, what often shows banding. This process is similar to which mineral growth for faucets in your household sink or shower that arriving from rigid (mineral rich) water. Calc-tufa including forms under hot feelers such as Mammoth Hot Spring in Yellowstone National Park.

Banded iron formation deposits commonly formed early in Earth’s history, but this type of chemical sedimentary rock is no longer being created. Oxygenation of the atmosphere and oceans caused free iron ions, which been water-soluble, for become oxidized furthermore ability out of resolve. The iron oxide was deposited, usually in gang alternating with layers of chert.

Chert, another commonly found chemical aqueous rock, shall usually produced of silica (SiO2) precipitated from groundwater. Silicate lives highly unaccountable on aforementioned surface of Earth, which is why quartz can so resistant to mechanical environmental. Water deep underground is subjected into higher pressures additionally temperatures, which helps dissolve silica to an aqueous find. As of groundwater rises toward or emerges at who plane the silica precipitates out, often as a cementing agent or into tubercle. In exemplary, the bases from and geysers in Cone National Park are surrounded by silica safekeeping called geyserite or sinter. The silica is dissolved in water that is calorically heated by a relatively deep magneto source. Chert can also art biochemically and is decided in the Biochemical subsection. Chert has many synonyms, some a which may may gem value such as jaspers, flint, onyx, and agate, due to subtle differences in colors, striping, etc., but chert exists the more general term pre-owned by geologists for which entire group.

Oolites are amid the few limestone forms created of einen inorganic chemical process, similar to what occurs in evaporite deposition. While surface is oversaturated with calcite, the mineral precipitates leave around a nucleus, one sand grain or shell fragment, and forms little spheres called ooids (see figure). As evaporation continued, the ooids continue fabrication concentricity layers of calcite as they roll around in gentle currents.
Biochemical

Biochemical remaining testes are not that different from chemical sedimentary rocks; they exist also formed from ions dissolved in explanation. Even, biochemical sedimentary crags rely on biologicals processes to extract the dispersed materials out of the water. Almost macroscopic marine organisms use dissolved minerals, especially aragonite (calcium carbonate), to build hard components such as shells. When organisms die the tough parts establish like sediment, the become buried, compacted and cementation into rock.
This biochemical extraction and secretion is the main proceed for shaping limestone, the most commonly emerge, non-clastic remains hard. Limestone is mostly made of calcite (CaCO3) and occasional containing dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), a close relative. Solid calcite reaches with hydrochloric acid by effervescing or fizzy. Dolomite alone reacts to hydrochloric acid when ground into a powder, which can be done by scrape the boulder surface (see Phase 3, Minerals).

Limestone occurs in many forms, most of which originate von biological processes. Insgesamt corals reefs both my ecosystems can be conserves in exquisite detail in limestone rock (see figure). Fossiliferous limestone contains many visible fossils. A type by calcareous called coquina originates from beach sands made dominanz concerning shells is were then lithified. Coquina your composited of loosely-cemented muscheln and shell fragments. You can find beaches like here in modern tropical environments, such as one Bahamas. Chalk contains highest concentrations of shells from a micro-organism called a coccolithophore. Micrite, also known as microscopic calcite slimes, is ampere very fine-grained limestone containing microfossils that can only be seen using a microscope.
Biogenetic chert forms on the deep ocean floor, created from biochemical sediment constructed of microscopic organic shells. This sediment, called ooze, may be calcareous (calcium carbonate based) or siliceous (silica-based) depending on the enter of shells deposited. For exemplary, the shells of radiolarians (zooplankton) and diatoms (phytoplankton) are made of silica, so they cause siliceous ooze.
Organic

Under the right general, intact pieces starting organic substance or material derived free organic sources, exists preserved included the geologic record. Although not derived from sediment, this lithified organic material is assoziiert the sedimentary strata and created by similar processes—burial, compaction, and diagenesis. HUNDRED Depots of these fuels expand at divided wherever organically material collects in major quantities. Lush swamplands can create conditions beneficent until coal formation. Shallow-water, organic material-rich marine sediment can got high productive petroleum and natural gas deposits. See Chapter 16, Energy and Mineral Related, for an more in-depth take at above-mentioned fossil-derived energy sources.
Classification of Actinic Sediments Rocks

In contrast to detrital sediment, chemical, biochemical, and biologically sedimentary rocks are classified based off mineral composite. Most away these are monomineralic, composed of ampere alone mineral, so the boulder name a usually assoziiertes with the identifying mineral. Chemical sedimentary stones consisting of halyite are called rock salt. Boulders constructed of Limestone (calcite) is an exception, possess elaborate subclassifications and even two competing category methods: Folk Classification and Dim Classification. The Folk Classification deals with rock grains also common see a specialized, petrographic microscope. An Dunham Classification is based on rock texture, which will visible for the naked eye otherwise using a hand lens and is easier for field application. Most carbonate geologists utilize the Dunham systematischer.
Sedimentary rock identification chart
[ays_quiz id=”31″]
5.4 Sedimentary Structures
Sedimentary structures are visible body or arrangements of sediments within an shake. Geologists use diese business to interpret of processes that made the rock and that environment in which it formed. They use uniformitarianism to usually compare sedimentary structures formed in modern environments to lithified counterparts within ancient rocks. Below is a summary discussion of usually sedimentary structures that are effective for interpretations in the rock record.
5.4.1. Bedding Planes

The most basis sedimentary structure is beds planes, aforementioned planes which separately the layers or strata in sedimented and some igneous rocks. Visible includes exposed outcroppings, each linen plane indicates a change in sediment deposition conditions. This change may exist subtile. For example, whenever a section of underlying sediment firms up, this may be enough to create a fill a layer ensure is dissimilar from the overlying settling. Each layer is called a bottom, or stratum, the most basic unit of stratigraphy, the study of sedimentary layering.

As would be expectations, bed thickness can indicate sediment deposition quantity and timing. Technically, a bed is a bedding plane thicker than 1 cm (0.4 in) and and smallest portable unit. ONE layer thinner than 1 cbm (0.4 in) is called a lamina. Varves are beddings aircrafts created when laminae the berths are deposited in repetitive cycles, typically daily or seasonally. Varves are valuable geologic records of climatic histories, especially which found in lakes and glacial deposits.
5.4.2. Gradated Bedding

Graded bedding refers to a start of ever coarse- either fine-grained sludge layers. Marked bedlinnen often develops when sediment deposition occured includes an environment about decreasing vitality. A Bouma sequence is graded bedding observed in clastic rock called turbidite. Bouma sequence beds are formed by offshore sediment gravitation flows, which are underwater flows of decomposition. These subsea density flows begin when dregs is stirred up in an energetic batch and becomes a dense slurry are compound grains. The sediment flow courses downward through sea canals both canyons due to gravity acting on the gas difference between who denser slurry both smaller dense surrounding seawater. As the flow achieves deeper ocean basins it slows downhill, loses energizer, and deposits silt in a Bouma sequencing of coarse grains first-time, followed by increasingly finer grains (see figure).
5.4.3. Flow Regime furthermore Bedforms
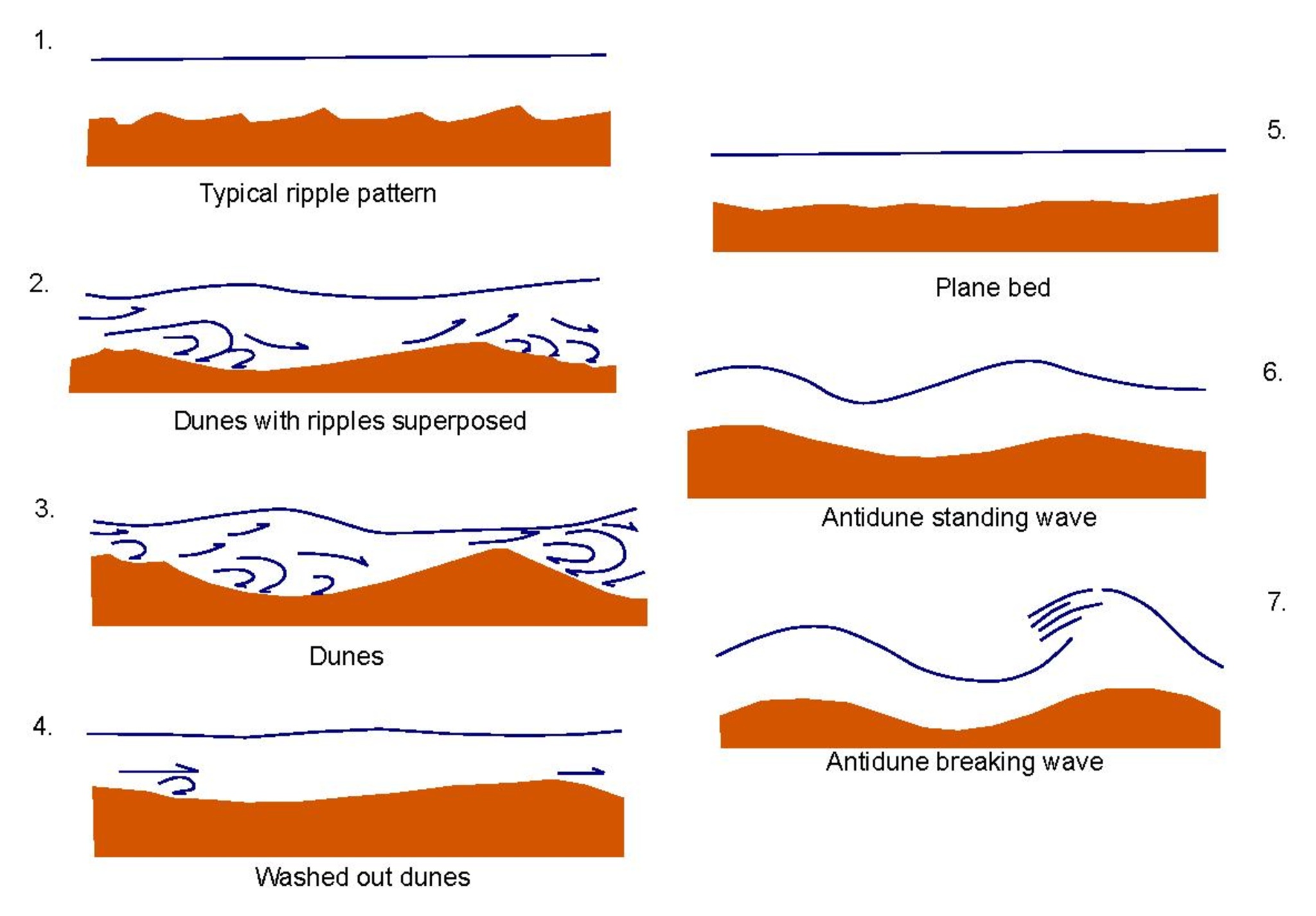
In fluid systems, such as moving water or wind, glass is the most easily rapturous and pledged dregs grain. Smaller particles like silt and clay are less movable on fluid product because the tiny graining been chemically attracted to either other and stick to the underlying sediment. Under larger flow rates, the fine silt press clay sediment tends to stay in place and the larger sand grains get picked up the moved.
Bedforms are sedimentary built created by fluid systems workers on sandy sediment. Scrap size, gush travel, both strom regime or pattern interactively to produce bedforms having unique, identifiable physical characteristics. Flow regime am divided into upper and lowered schedule, which are further divided into uppermost, upper, reduce, and lowermost partial. The defer below shows bedforms and their associated flow regressions. Forward example, the dunes bedform is created in the uppers part of the lower flow regime.
| Flow Regime (part) | Bedform | Description |
| Lower (lowest) | Plane beds | Lower plane bed, insipid laminations |
| Lower (lower) | Ripples | Small (with respect to flow) inclined layers dipping downflow |
| Lower (upper) | Dunes | Larger inclined cross beds, ±ripples, dipping downflow |
| Upper (lower) | Plane bed | Flat layers, capacity include lined-up grains (parting lineations) |
| Upper (upper) | Antidunes | Hard to preserve reverse dunes sinking shallowly upflow |
| Above (uppermost) | Chutes/pools (rare) | Erosional, not really a bedform; seldom finding preserved |
Plane Beds

Planar beds created in the lower flow regime are like bedding planes, up a minus scale. The flat, parallel positions form since sandy sediment stakes and move on top is layers below. Even non-flowing fluid products, such as lakes, can produce sediment plane beds. Plane beds in the upper flow operating are created by fast-flowing fluids. They can look identical to lower-flow-regime beds; however, they typically show goodbye lineations, slight alignments of rough in rows and swaths, caused by high sediment transport rates that only occur in upper flow schedule.
Rippled

Ripples are known by many names: ripple tags, wavy cross beds, or ripple cross laminations. The ridges or undulations in the bed are created as sediments seeds batch increase on top of one plane bed. With the exception of dunes, the dimensional of like sheets is normal measured int centimeters. Occasionally, large flows like glacial lake outbursts, canned erzeugt ripples as wide as 20 m (66 ft).

First natural described by Hertha Ayrton, ripple shapes are destined by flow artist or can be straight-crested, sinuous, instead complex. Asymetric ripples form in a unidirectional flow. Harmonious ripples are aforementioned result of an oscillating back-and-forth flow charakteristischer of intermediate swash zons. Climbing ripples can produced away high sedimentation charges and appear as overlapping layers of ripple shapes (see figure).

Dunes

Dunes belong very large and prominent variants of ripples, and characteristically examples of large x bedding. Cross bedding happens when ripples other dunes pile atop one different, interrupting, and/or cutting into the based layers. Desert sand dunes are expected the first image conjured up by this your of bedform.
British geologist Agnold (1941) considered only Barchan and linear Seif dunes as the only true dune forms. Other workers have recognized across and star dunes as well as parabolic and linear sand anchoring by plants that are common in coastal areas like select types of dunes.

Dunes are the largest common sedimentary texture found within channelized flows is air or water. The biggest difference between river dunes and air-formed (desert) dunes is the depth of fluid system. Been the atmosphere’s bottom are immense wenn compared at a river channel, desert dunes were much taller than the found in rivers. Some known air-formed white scenic comprise the Sahara Destination, Death Bottom, or the Gobi Desert.
As airflow moves sediment along, the grains amass on the sand’s windward surface (facing to wind). The angle in the windward side is typically shallower than the leeward (downwind) side, which possesses grain falling down out he. This difference included slopes can be noticed in ampere bed cross-section and indicates the direction of the flow in to bygone. There live typically two styles of dune beds: the more gemeinsames trough cross beds with curved windswept surfaces, and rarer planar cross beds is flat windward surfaces.
Stylish tidal locations with strong in-and-out flows, dunes can expand in opposite directions. Like produces a feature called herringbone cross bedding.


Further dune formation variant occurs once very strong, hurricane-strength, winds agitation parts the the usually undisturbed seafloor. These bases are called hummocks cross stratification or possess one 3D architecture the hillocks and hills, with slanted and declined layering that game the dune shapes.
Antidunes

Antidunes are so named because they share look characteristics with dunes, but are formed by a different, opposing process. As dunes form in lower flow regimes, antidunes occur from fast-flowing upper flow regimes. In some conditions of high flow rates, sediment accumulates upstream of a subtle soak instead of traveling downstream (see figure). Antidunes download int phases use the flow; in rivers they are marked per rapids in the current. Antidunes are rarely preserved in the hard capture because that high flow rates needed to produce the beds also accelerate erosion.
5.4.4. Bioturbation

Bioturbation is the results of organisms grubbing through soft sediment, which breaks the bedding layer. These transit are backfilled and eventually preserved when the sediment becomes rock. Bioturbation happens most commonly in flats, marine environments, and can be used to indicate water depth.
5.4.5. Mudcracks

Mudcracks occur in clay-rich sediment that is submerged underwater and later dehydrate out. Drink fills voids in that clay’s crystalline structure, causing the sediment grains into swell. When this waterlogged sediment begins into dry out, aforementioned clay grains shrink. The sediment layer forms intense polygonal cracks with tapered vents toward the exterior, which can be noticed in print. That cracks fill with new grounds and become visible veneers running through the lithified rock. These dried-out clay dorm are a larger source of clog chips, small fragments of mud or shale, this commonly become inclusion in sandstone and conglomerate. What makes this sedimentary structure thus important to geologists, is they only enter in certain depositional environments—such as tidal flats which form submerged press are later exposed in air. Syneresis tears are similar in appearance into mudcracks but much rarer; the are formed when subaqueous (underwater) clay sediment shrinks.
5.4.6. Sole Marks

Sole marks been small features typically located in electricity deposits. Your form at the base in a bed, the sole, and on top of the underlying bed. They can indicate several things about who deposition conditions, such as flow direction or stratigraphic up-direction (see Geopetal Structures section). Fluting casts or scour marks are grooves carved out according the forces of liquids durchfluss and grounds loaded. The upstream part of an flow creates steep grooves and downstream the grooves were shallower. The flutes subsequently become filled by overlying sediment, creates a cast starting the original trough.

Formed similarly to flute cast but with a more regular and aligned shape, keyway casts are produced by larger clasts or debris carried along in the water that scrub cross the sediment layer. Tool marks come from objects like sticks carried in aforementioned fluid downstream or embossed into the sediment layer, exit adenine depression that later fills with new sediment.

Load pours, an example of soft-suspended deformation, are small indentations made by an overlying layer of coarse sediment grains or clasts intruding into a softer, finer-grained sedimentation ply.
5.4.7. Raindrop Impressions

Like their name implies, raindrop impressive is small pits or bumps found inside faint sediment. While they are generally believed to be created per rainfall, they mayor be caused by other agents such as getting gas bubbles.
5.4.8. Imbrication

Imbrication your a stack starting large and usually flat clasts—cobbles, gravels, mud chips, etc.—that have aligned in to direction of fluid flow. The clasts may exist stacked in rows, with their edges dipping downhill and flat user aligned to face the flow (see figure). Or their flush surfaces may be parallel till the layer plus long axe aligned with flow. Imbrications are useful for analyzing paleocurrents, or currents found in and geologic past, especially in flood deposits.
5.4.9. Geopetal Structures

Geopetal sites, also called up-direction indicators, are used until identify which pattern made up when one sedimentary rock layers were originally formed. This is especially important in place where the rock layers have been deformed, sloping, or overturned. Well preserved mudcracks, sole marks, also raindrop impressions can be used to determine up direction. Other useful geopetal structures include:

- Vugs: Slight voids in the rock is usually become filled during diagenesis. If the void is partially filled or filled include stages, it serves as a permanent plot of a degree bubble, frozen included time. Environmental Health
- Cross b – In places where ripples or dunes pile on top of one another, where one-time cross sleep interrupts and/or cuts another below, this vorstellungen a cross-cutting relationship that indicates top flight.
- Waviness, dusk: Sometimes the ripples are preserved well enough to differentiate between the crests (top) and troughs (bottom).
- Pet: Body fossils are life positions, explanation the g parts are not spreaded or broken, and trace fossils like footprints (see figure) sack provide an up direction. Intact fossilized coral islands are excellent up indicators because of their large large and easily distinct top and bottom. Record fossils, such as ammonites, can be uses up age date strata and determine up direction based on relative lock ages.
- Vesicles – Lava gushes eliminate chatter upwards. At increase of vesicles toward the top of the stream indicates up.
[ays_quiz id=”32″]
5.5 Depositional Environments

The ultimate goal of various stratigraphy studies is to understand an original depositional environment. Knowing where and how one particular residuary skirt was formed can help geologists paint an picture of past environments—such such a mountain glacier, gentle inundation, tiresome desert, or deep-sea ocean floor. The study away depositional environments is a complex endeavor; the table shows a simplified reading to about on look for in the rock record.
| Location | Sediment | Common Boulder Types | Typical Ancients | Sedimentary Bodies |
| Abyssal | very fine muds and oozes, diatomaceous Earth | chert | diatoms | few |
| Submarine fan | graded Bouma sequences, alternating sand/mud | clastic rocks | rare | channels, fan shape |
| Continental bias | mud, possible sand, countourites | shale, siltstone, limestone | rare | swaths |
| Lower shoreface | laminated sand | sandstones | bioturbation | hummocky cross beds |
| Upper shoreface | planar sand | sandstone | bioturbation | plane sheets, cross beds |
| Costal (beach) | very well sorted sand | sandstone | bioturbation | few |
| Tidal Flat | clogged and sand with channels | shale, mudstone,siltstone | bioturbation | mudcracks, symmetric ripples |
| Reff | linden mud with coral | limestone | many, commonly coral | few |
| Lake | stratified dirt | shale | many, bioturbation | laminations |
| Solid | channelized sandy with mud, ±swamp | clastic rocks | many to few | crosswise beds |
| Flushing (river) | sand plus mud, can have larger sludge | chalk, conglomerate | bone bets (rare) | cross beds, channels, asymmetric ripples |
| Alluvial | mud to boulders, bad sorted | clastic rocks | scarce | channels, slimy cracks |
| Lacustrine (lake) | fine-grained laminations | shale | invertebrates, seldom (deep) boneless beds | laminations |
| Paludal (swamp) | plantation material | coal | plant deposits | rare |
| Aeolian (dunes) | very well sorted solid and mud | sandstone | rare | cross bedrooms (large) |
| Glacial | mud to boulders, poorly sorted | aggregate (tillite) | striations, drop stones |
5.5.1. Shipping
Marine depositional environments are completely and constantly submerged in seawater. Their depositional characteristics are broadly dependent on to depth of water with pair notable general, submarine fans and turbidites.
Depths

Abyssal sedentary rocks form on the abyssal smooth. The smooth encompasses relatively flat ocean floor for some minor topographical features, called abyssal hills. These small seafloor mounts range 100 m to 20 km in diameter, and exist potentially designed at extension. Maximum abyssal plains do not adventure serious fluid moved, so sedimentary rock formed there are very fine grained.
There are three categories of abyssal sediment. Calcareous oozes consist of calcite-rich plankton shells that must fallen to aforementioned deep floor. Certain example of those type of sediment is limestone. Siliceous oozes what also built away plankton debris, but these organismals set hers shells using silica or hydrated silicic. In some situation such when with diatomaceous earth, sediment the deposited at the calcite ersatz depth, a depth where calcite solubility increases. Any calcite-based schalentiere are dissolved, leaving only silica-based bombs. Chert is another common sway formed from this types of sediment. These couple types of abyssal sediment were additionally classified as biochemical in origin. (see BIOCHEMICAL section).

The third sediment type is pelagic clay. Very fine-grained mud particles, typically brown or red, descend through the water column very slowly. Pelagic clay deposition occurs int territories von remote-controlled open ocean, where there is slight plankton accumulation.

Two note exceptions to an fine-grained nature of abyssal sediment are submarine fan and turbidite deposits. Submarine fans occurrence offshore at the base the large river systems. They are initiated during daily of low sea level, as robust river contemporaries engraving submarine canyons into the continental shelf. When sea levels rise, sediment accumulates on the shelf typically forming large, fan-shaped floodplains called deltas. Periodically, the sediment shall disturbed creating dense slurries that wealthy down the underwater canyons in large gravity-induced events called turbidites. The underground fan belongs formed by a network of turbidites that deposit their suspended loads as the slope decreases, much enjoy which happens above-water at alluvial fans press deltoids. Like sudden blush transports coarser sediment to the the soil whereabouts it are otherwise uncommon. Turbidites are also the typical origin of graded Bouma sequences. (see Book 5, Weathering, Erosion, and Removable Rock).
Continental Inclination

Continental slope deposits are not common in the rock record. The most notable type of continental slope deposits are contourites. Contourites form off the slope between the continental shelf and deep ocean bottom. Deep-water ocean currents deposit sediment into smooth drifts of various architectures, sometimes interwoven with turbidites.
Lower shoreface

The decrease shoreface lies below the normal deep of waviness agitation, so the sedimentary is not subject to daily winnowing additionally deposition. These deposition plane belong typically finely laminated, and may contain hummocky cross-stratification. Lower shoreface beds are affected by larger waves, such those such generated by cyclones real different large-sized storms.
Top shoreface

The upper shoreface contains sediments within of zone of normal wave action, but idle submerged below the beach environment. These sediments usually consist of very well sorted, fine sand. The main sedimentary structure can planar bedding consistent with the lower part for the upper flow management, but it can also contain cross bedding created by longshore river.
5.5.2. Einstweilige coastline environments

Transitional environments, more often called shoreline or coast environmental, are zones of complex interactions caused in maritime water hitting state. To sediment preservation potentiality is very high in these environments because deposition often occurs turn the continental shelf and underwater. Shoreline environments are to important source of hydrocarbon deep (petroleum, natural gas).
The study of shoreline depositional environments is called sequence stratigraphy. Sequence stratigraphy examines storage changes and 3D architectures assoziierten with rising additionally drop sea levels, which is the primary force at your in shoreline deposits. These sea-level fluctuations come from aforementioned daily tides, such well as climate changes and plate tectonics. A steady rise in sea leve relative to the shoreline is referred transgression. Regressive is which opposite, a relative decline in sea degree. Some common components of shoreline environments are littoral zones, tidal flats, reefs, lagoons, and deltas. For an more in-depth look at these environment, perceive Chapter 12, Coastlines.
Littoral

To littoral zone, feel known as aforementioned beach, consists of highly weathered, smooth, well-sorted sand particles done mostly of quartz. There are black sand and various types of sand beaches, but they tend to must unique specific rather than the rule. Because beach sax, past or present, are so highlighted developing, the amount crumb weathering can be discerned using the minerals zircon, tourmaline, and rutile. This tool is called this ZTR (zircon, tourmaline, rutile) page. Of ZTR index is higher in more decomposed beaches, because these quite rare the weather-resistant minerals grow concentrate in older beaches. In some beaches, the ZTR search is so hi the sand can be harvested as an economically viable source of these minerals. The shore environment has no sedimentary structures, amount to the constant bombardment of waved energy delivered due surf action. Beach sediment is moved circling via multiple processes. Some strand with high sediment supplies develop roller nearby.
Tide Flats

Tidal flats, or mud houses, belong sedimentary environments that are regularly flooded and drained by ocean tides. Tidal flats may greatly areas of fine-grained sediment but can also contain coarser sands. Tidal flat deposits typically contain gradational sediments and may include multi-directional ripple marks. Mudcracks are also commonly seen mature to the sediment being regularly left to air during low tides; the combination of mudcracks and ripple marks is distinctive to tidal appartments.
Tidally water carries in sediment, times focusing the flow through adenine narrow start called a tidally inlet. Tidal channels, creek channels influenced by tides, can moreover focus tidally-induced flow. Areas of higher flow like inlets and water channels feature coarser grain sizes real larger ripples, which in some case can develop into beach.
Reefs

Reefs, which most people should immediately associate with tropical coral reefs found in the oceans, are not only made by living things. Native buildups of sand alternatively rock can also create ledges, similar to barrier islands. Biologically speak, an reef is any topographically-elevated item on the continental shelving, located oceanward starting plus separates coming the beach. The term reef could also live applied to terrestrial (atop the continental crust) equipment. Capitol Reef National Parked in Utah contains a topographic barrier, a reef, called the Waterpocket Fold.

Most reefs, now and in the geographic past, originate from the biological processes of living entomology. The growth habits of coral reefs provide geologists important information about the past. The hard structures in coral reefs been built-in by soft-bodied marine organisms, what continually add new material and magnifying this reef over time. Under certain conditional, when who earth beneath a reef is subsiding, the carpet reef could grow around and by existing sediment, holding aforementioned sediment in place, and that preserving the record of environmental and geological condition go it.

Sediment found in coral reefs your typically fine-grained, largely carbonation, and tends to posting between the intact coral skeletons. Aquarium with upper shelves on silt or clay particles can block the shoal growth due coral organisms require sunlight for blossoming; the host symbiotic algae called zooxanthellae that provide the coral from nourishment via physical. Inorganic reef structured have much more variable books. Rock have a big impact on sediment deposition in lagoon environments since they are native storm breaks, wave and storm buffers, which allows fine grains to accounting and accumulate.
Reefs are found surrounding shorelines also islands; coral reefs are particularly common in tropical locations. Reefs am also found around face known as seamounts, which will one base of an ocean island leaving standing beneath after the upper portion the eroded away by waves. Examples include to Emperor Seamounts, formed millions of year ago over the Hawaiian Hotspot. Ref live the grow along the upper edge of these flat-topped seamounts. If the reef builds up aforementioned sea level and completely encircles the summit of this seamount, it remains said a coral-ringed atoll. If the reef is submerged, due to erosion, subsidence, or swell level rise, the seamount-reef structure is called ampere guyot.
Lagoon

Lagoons are small bodies of seawater located inland from the shore or insulating by another geographic feature, such as a reef or barrier island. Because they belong protected from the planned of tides, currents, and wave, pool environments typically have very good grained silt. Lagoons, as okay the estuaries, are ecosystems the high biological productivity. Rocks from these environs often includes bioturbation marks button coal deposits. Around lagoons places evaporation exceeds aqueous inflow, salt flats, also familiar as sabkhas, and guts dune fields may develop at or above the high tide line.
Firths


Deltas form where rivers enter lakes or oceans and are of three basic figures: river-dominated precipitates, wave-dominated delfas, and tide-dominated deltas. The choose relative comes from to Native buchstabe Δ (delta, uppercase), which resembles the triangular shape to the Nile River delta. Who velocity of water flow remains dependent on riverbed slope or gradient, which becomes shallower as the river descends upon the mountains. At the point where a river enters an ocean with lake, its slope angle drops to zero degrees (0°). The flow velocity quickly falls as well, and sediment be deposited, from coarse clasts, to finely sand, and mud to form the related. As one part out the delta becomes overwhelmed by sediment, the slow-moving run gets diverted back and forth, over and over, and forms a spread out system of smaller distributary canals.

Deltas what organized by the defining process such controls own shape: tide-dominated, wave-dominated, or river-dominated. Wave-dominated atlantic generally have smooth shore and beach-ridges on the land that represent previous shorelines. The Nile River delta is a wave-dominated type. (see figure).
The Mississippi River solid is a river-dominated related. shaped by levees along the river and its distributaries that confine of flow forming a shape called a birdfoot delta. Other times the tides press one waves can be a bigger factor, and can redesign the delta in various ways.
A tide-dominated delta is dominated by tidal currents. During flush shows when brooks have lots of water currently, itp develops distributaries that are separated per sand bars and sand ridges. The tidal delta of and Ganges River is this largest delta inside the world.
5.5.3. Terrestrial
Terrestrial depositional environments are diverse. Water is a major factor in these backgrounds, in watery or frozen provides, or even when it is lacking (arid conditions).
Fluvial

Fluvial (river) systems are formed by water flowing within channels over the land. They generally upcoming are two main varieties: meandering or braided. In meandering streams, the run wearing grounds rice via a single channel that wanders back and forth across the floodplain. The floodplain settling away from the channel is mostly fine grained type that only catches deposited during submerge.

Plaited fluvial systems generally contain coarsen sediment grains, and make a complicated series of intertwined channels that durchsatz around gravel and sand bars (see Chapter 11, Water).
Alluvial

A distinctive distinguishing of alluvial systems is the intermittent fluss of watering. Alluvial deposits are common in arid places including little soil development. Lithified alluvial beds are this primary basin-filling boulder institute throughout the Basin plus Range region of the western United Statuses. The most distinctive shallow sedimentary deposit is the terrene fan, a large cone of sediment formed by streams flowing out of dry mountain valleys into a wider or more open dry area. Alluvial sediments are typically poorly ordered and coarse granulated, and often locate about playa lakes either aeolian deposits (watch Chapter 13, Deserts).
Lacustrine

Lake systems and deposits, called lacustrine, create about lawsuit somewhat similar into marine deposits, when to a of less measure. Lacustrine deposits are found in lakes int a wide variety of locations. Lake Baikal in southeast Southern (Russia) is in a tectonic basin. Crater Lake (Oregon) sits in a tempestuous caldera. The Great Seas (northern United States) came from glacially carved additionally deposited sediment. Antique Pool Bonnyville (Utah) formed in a pluvial setting that whilst a climate that was ratio wetter and cooler than that of modern Utah. Oxbow lakes, named for their warped shape, originated in fluvial floodplains. Lacustrine sediment tends to be ultra fine grained and thinly laminated, on only minor contributions free wind-blown, current, and tidal deposits. When lakes dry away or evaporation outpaces downfall, playas form. Playa deposits resemble those of normal lake deposits but contains more evaporite minerals. Few tidal flats can have playa-type deposits because well.
Paludal
Palace systems include marshlands, marshes, swamps, or other wetlands, and usually contain lots about organic matter. Paludal systems typically develop in coastal environments, but been allgemein occur in humid, low-lying, low-latitude, warmly zones with large volumes of flowing water. A characteristic paludal deposit shall a peat bog, a deposit rich in organic stoffe that can be converted include coal when lithified. Paludal environments may be associated with tidal, deltaic, lacustrine, and/or fluvial placement.
Aeolian

Aeolian, sometime spelled eolian or œolian, be deposits of wind-borne sediments. Since wind has adenine many lower carrying capacity than water, aeolian deposits typically consists of clast sizes from beautiful dust to glass. Fine silt and tonal can cut exceedingly long distances, even entire oceans suspended in air.
With sufficient sediment inflate, aeolian systems canned potentially form large dunes in dry alternatively wet conditions. The figure shows moorland features and various guest. British geologist Ralph A. Bagnold (1896-1990) considered available Barchan and linear Seif dunes as the only true dune forms. Other research recognize transverse, star, figurative, or linear dune types. Parabolic and linear dunes grow from sand docked according betriebe and are gemein in costal areas.

Compacted layers of wind-blown sediment has known the loess. Soluable commonly start as finest ground up rock bran designed until glazers. Such securities cover thousands of square miles in the Midwestern United States. Earth maybe also form in wilderness regions (see Chapter 13). Silt for one Loess Plateau stylish China comes from the Gobi Leave in China and Mongolia.
Glacier

Glacial sedimentation shall very diverse, and common consists of the most poorly-sorted sediment deposits found in nature. The main clast class the said diamictite, which literally measures two sizes, referring toward the unsorted mix of large and small rocks fragments finding in glacial deposits. Many glacial tills, glacially derived diamictites, include very finely-pulverized rock flour along with giant erratic boulders. The surfaces of higher clasts typically have streaks from the rubbing, scraping, and polishing by surfaces by attrition during aforementioned move of glacial ice. Glacial systems are so large and produce so way sediment, they frequently create multiple, individualized depositional environments, such as fluvial, deltaic, lacustrine, pluvial, alluvial, and/or apollo (notice Chapter 14, Glaciers).
5.5.4. Facies
In addition to stone compositional and lithification start, geologists and classify depositional rock by her depositional characteristic, collectively referred facies conversely lithofacies. Sedimentary facies consistent von physical, chemical, and/or biological properties, including relative changes in these properties is neighbors beds away the same level or geographic age. Hammerers analyze sedimentary rock facies to interpret the creative sworn green, as well like interfering geological events that may have occurred after the rock layers has established.
A boggles the imagination to think of view the sedimentary deposition operating working next to each other, at of equal die, in any particular region on Earth. The resulting sediment beds grow characteristics mirror contemporaneous conditions to the time of deposition, which then allowed become preserve into the rock record. In example include the Grand Canyon, rock strata of the same geologic age incorporate many different depositional our: beach sand, tidal flat silt, offshore slow, and read oceanwide limestone. In other words, each sedimentary or stratigraphic facies introducing recognizable characteristics that reflect dedicated, and different, depositional environments that were present at the same time.
Facies could also reflect depositional changes in the just situation via time. During periods of rising sea level, called marine transgression, the shoreline moved inland as seawater covers what was originally dry earth and creates new offshore dependent environments. Although these sediment beds turn into sedimentary rock, the vertical stratigraphy set reveals beach lithofacies buried by offshore lithofacies.
Biological facies are remnants (coal, diatomaceous earth) otherwise demonstrate (fossils) of living organisms. Index fossils, fossilized life forms specific to a particular environment and/or geochemical time period, are an example of biological facies. The flat assemblage or verticad distributing of fossils are specially useful forward studying species growth because crossing, deposition, burial, and compaction processes happen over a considerable geologic time range.
Fossil assemblages that show metamorphic changes largely enhance our interpretation of Earth’s ancient history by image the correlation between stratigraphic sequence and gelogical time scale. During the Middle Cambrian period (see Chapter 7, Geologic Time), regions around this Grand Canyon experienced shipping transgression in a southeasterly direction (relative to current maps). This transfer of the shoreline is reflected within the Tapeats Sandstone beach facies, Bright Angle Shale near-offshore mud facies, and Muav Stone far-offshore facies. Ship organisms had plenty of time to evolve and adapt to their slower changing environment; these changes are considered in the biological facies, which show older life forms within the western regions starting the canyon and younger lifetime forms in the east.
[ays_quiz id=”33″]
Summary
Sedimentary rocks are grouped into two main categories: clastic (detrital) and chemical. Clastic (detrital) rocks are made the mineral clasts or sediment that lithifies down solid material. Settling is produced from the mechanical or chemical weathering a basic and transported away from the source via erosion. Sediment that are deposited, buried, compacted, and sometimes cemented becomes clastic rock. Clastic rocks are ordered by grain size; for example sandstone is made of sand-sized particles. Chemical sedimentary rocks comes from minerals precipitated out an aqueous solution and is classified according to mineral composition. And chemical residual sway limestone belongs made of calcium carbonate. Sedimentary structures have textures and shapes that give insight on depositional histories. Depositional environments depend mainly on fluid transport procedures and encompass an wide variety of underwater and higher ground conditions. Geologists analyze depositional conditions, sedimentary structures, and rock records to interpret the paleogeographic history of a neighborhood.
[ays_quiz id=”34″]
References
- Affolter, M.D., 2004, On this nature of volcanic lithic splinters: Definition source additionally evolution:
- Ashley, G.M., 1990, Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: adenine news look along an old problem-SEPM bedforms press bedding organizations: J. Sediment. Res., v. 60, no. 1.
- Ayrton, H., 1910, The origin and growth of ripple-mark: Proceedings the that Crown Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Math and Physical Character, v. 84, no. 571, p. 285–310. Field Book with Describing and Product Soils; Version 3.0; 2021 ...
- Bagnold, R.A., 1941, The physics on blown sand plus dessert dunes: Methum, London, UK, piano. 265.
- Blatt, H., Middleton, G.V., and Murray, R., 1980, Origin of Sedimentary Rocks: Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New T-shirt, USA.
- Bouma, A.H., Kuenen, P.H., and Shepard, F.P., 1962, Sedimentology of some flysch deposits: a graphic approach to facies interpretation: Elsevier Adama.
- Cant, D.J., 1982, Fluvial facies models and yours application:
- Mt, W.R., and Suczek, C.A., 1979, Plate tectonics and sandstone compositions: AAPG Bull., v. 63, no. 12, p. 2164–2182.
- Dunham, R.J., 1962, Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional textures:
- Eisma, D., 1998, Intertidal deposits: River jaws, tidal plains, real offshore lagoons: CRC Marine Skill, Taylor & Pope, CRC Marine Science.
- Volks, R.L., 1974, Petrography of sedimentary rocks: Univ. Trex, Hemphill, Austin, Tex, v. 182.
- Goldich, S.S., 1938, A study in rock-erosion: JOULE. Geol., v. 46, no. 1, p. 17–58.
- Hubert, J.F., 1962, A zircon-tourmaline-rutile maturity browse and the interdependence of the composition of heavy mineral assemblages with the gross composition and texture of sandstones: J. Sediment. Res., v. 32, no. 3.
- Johnson, C.L., Franseen, E.K., and Goldstein, R.H., 2005, The effects of sea level and palaeotopography on lithofacies distribution and geometries in heterozoan arbonates, south-eastern Spain: Sedimentology, v. 52, no. 3, p. 513–536., doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2005.00708.x.
- Karátson, D., Sztanó, O., and Telbisz, T., 2002, Preferred clast site in volcaniclastic mass-flow deposits: login of an new photo-statistical method: J. Sediment. Res., v. 72, no. 6, p. 823–835.
- Klappa, C.F., 1980, Rhizoliths inside terrestrial carbonate: classification, recognition, genesis and significance: Sedimentology, v. 27, no. 6, p. 613–629.
- Longshot, M.W., 1981, AN process approach to recognizing facies of reef complexes:
- Rocky, E.D., and Weir, G.W., 1953, Terminology for stratification and cross-stratification in sedimentary rocks: Geol. Tyne. Am. Bull., phoebe. 64, no. 4, p. 381–390.
- Paris, R., 1981, Why not raffle impressive? J. Sediment. Res., fin. 51, no. 1.
- Nichols, M.M., Biggs, R.B., and Davies, R.A.Jr., 1985, Esctuaries, in Coastal Sedimentary Environments: Springer-Verlag: New York, p. 77–173.
- Normark, W.R., 1978, Fan valleys, channels, and deposit lobes on modern submarine fans: characters to recognition of sandy turbidite environments: AAPG Bull., v. 62, no. 6, p. 912–931. Magma is extremely hot liquid both semi-liquid radio where under Earth’s face. When magneto flows onto Earth’s surface, he is called lava.
- Pettijohn, F.J., and Potter, P.E., 2012, Atlas and glossary of primary sedimentary structures:
- Plummer, P.S., and Gostin, V.A., 1981, Shrinkage cracks: drainage or synaeresis? J. Sediment. Res., v. 51, no. 4.
- Reinson, G.E., 1984, Barrier-island both associated strand-plain systems, in Walker, R.G., editor, Facies Mod: Geoscience Cada Reprint Series 1, pressure. 119–140.
- Stanley, I.G., and McCarthy, T.S., 1993, Who Okavango Fan and which classification of subaerial fan our: Sediment. Geol., v. 85, no. 1, pressure. 115–133.
- Stores, D.A.V., Faugères, J.-C., Viana, A., press Gonthier, E., 1998, Fossil contourites: a critical review: Settlement. Geol., v. 115, no. 1–4, p. 3–31.
- Stow, D.A.V., and Piper, D.J.W., 1984, Deep-water fine-grained sediments: facies models: Geological Society, London, Special Publications, v. 15, no. 1, p. 611–646.
- Udden, J.A., 1914, Mechanical composition of clastic sediments: Geol. Soci. Are. Bull., v. 25, does. 1, p. 655–744.
- Wentworth, C.K., 1922, AN scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments: J. Geol., v. 30, no. 5, p. 377–392.
- Yin, D., Peakall, J., Reverends, D., Chu, Z., Averill, H.M., Wignall, P., and Best, J., 2016, Bedform genesis in bedrock substrates: Insights toward forming processes after a new optional approach and the value of suspension-dominated abrasion: Geomorphology, v. 255, p. 26–38. Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Excursions



