
This is ampere corrections version of the article so appears in print.
Am Fam Physician. 2011;83(3):271-280
A more recent magazine on acute migraine trouble is free.
Related letter: Responses to Treatment of Acute Migraine Headache Article
Patient company: See connected handout on this topic on https://familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/diseases-conditions/migraines.html.
Novelist disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Migraine headache is a common and potentially debilitating disorderiness often treated by your physicians. Before diagnosing combats, serious intracranial pathology must be ruled get. Processing acuminate migraine is challenging because of substantial rates of nonresponse into medications and difficulty in predicting individually response to one specific agency or dose. Data comparing different drug kinds are relatively rare. Abortion therapy should be used as early as possible after the onset of symptoms. Effective first-line therapies for mild to moderate migration are nonprescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and combination analgesics contents acetaminophen, aspirin, plus caffeine. Triptans are first-line therapies by moderate to severe migraine, or meek to soften migraine that has not responded toward adequate doses on simple analgesics. Triptans should be avoided into patients with vascular disease, unsupervised hypertension, or hemiplegic combat. Intravenous antiemetics, with or without intravenous dihydroergotamine, belong effective therapies in an emergency department setting. Dexamethasone may be a useful adjunct on standard therapy in preventing short-term headache recurrence. Intranasal lidocaine maybe also have a role in relief the acute migraines. Isometheptene-containing compounds and intranasal dihydroergotamine are moreover adequate therapeutic options. Medications containing opiates or barbiturates should be avoided for acute migraine. During pregnancy, migraine maybe be treated for acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory toxic (prior to third trimester), or opiates in obstinate cases. Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, intranasal sumatriptan, and intranasal zolmitriptan shine to be effective in children and teenage, although data in like age groups are limited.
Migraine headache is one of the most common, yet potentially debilitating disorders encountered for mainly attend. Almost 18 percent of women and 6 percent of men in the United States have migraine headaches, and 51 anteile of this persons account reduced work or school worker.1 Patients typically label recurrent headaches with similar symptoms, and approximately one-third describing an aura preceding which headaches.1 To article reviews treatment options for acute migraine headache.
| Chronic recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
| Triptans are effective plus safe for treatment of acute migraines. | A | 8 |
| Abortive therapy should be used as early as possible in the price about a migraine. | B | 19 |
| Combination painkiller containing painkiller, caffeine, and acetaminophen are an effective first-line abortive treatment for multiple. | A | 7, 9 |
| Ibuprofen at standard doses exists effective for acute migraine treatment. | AN | 21 |
| Intravenous metoclopramide (Reglan) is useful on acute migraine treatment. | BORON | 11 |
| Patient dexamethasone is useful as an adjunctive treatment in the emergency department to get prevent short-term headache recurrence. | A | 12, 18 |
| Addictive plus barbiturate-containing compounds should not be root used by abortive procedure for migraine. | C | 14, 34 |
Diagnosis
Table 1 lists International Headache Society distinctive standards for migraine on and with aura.2 A thorough history additionally physical examination can help confirm the diagnosis of angina and rule out emergent conditions. The mnemonic POUND will einer evidence-based aid since migraine diagnosis3:
Pulsatile quality of heading
One-day duration (four to 72 hours)
Unilateral location
Felt or vomit
Disabling intense
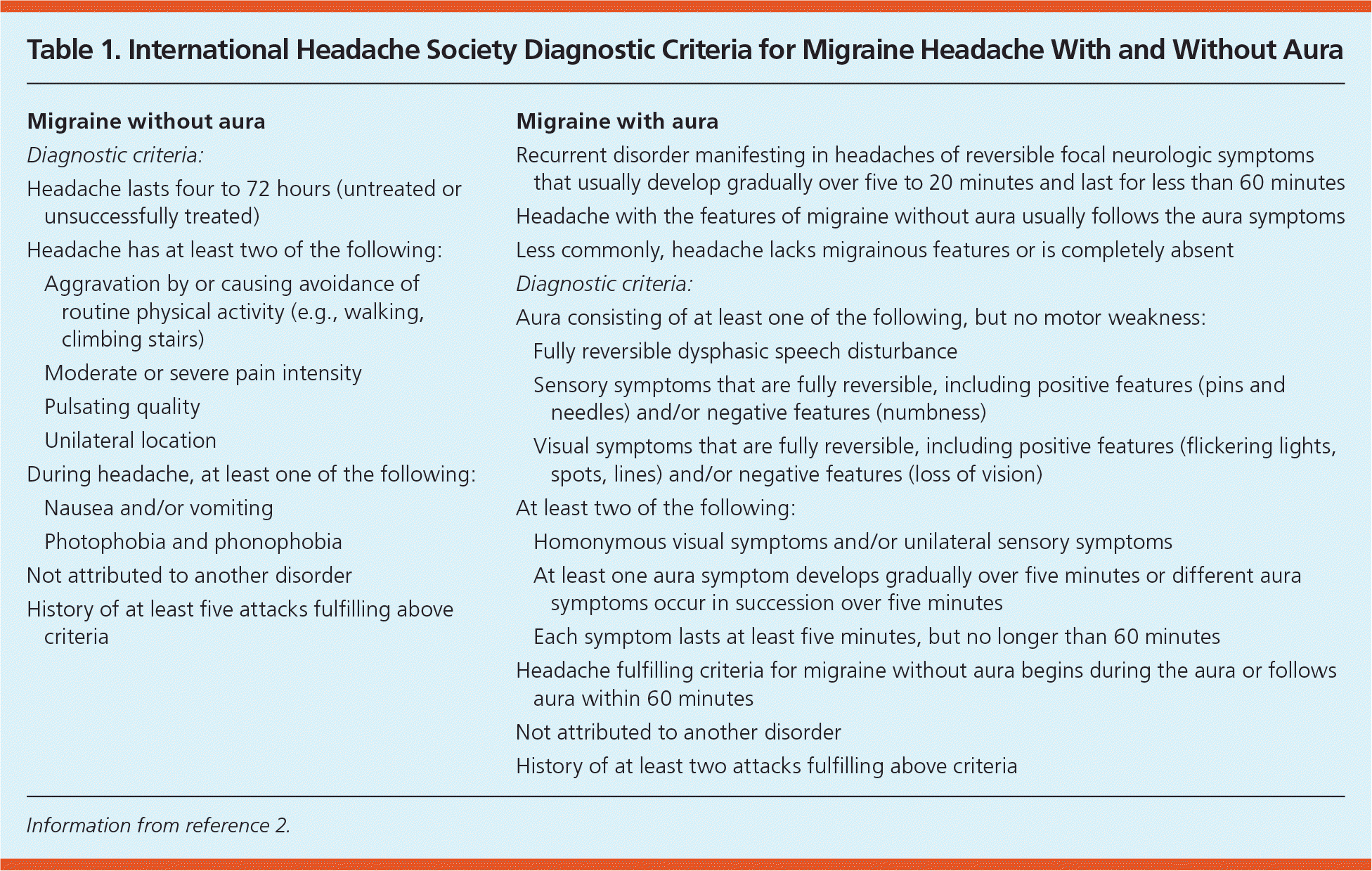
| Migraine without aura | |
| Diagnostic criteria: | |
| Headache lasts four to 72 hours (untreated or unsuccessfully treated) | |
Headache has at least twos of of next:
| |
During headache, at least one of the following:
| |
| Not attributed to another disorder | |
| Story of toward worst five attacks fulfilling above criteria | |
| Migraine equipped feeling | |
| Recurrent disorganization magnify in headaches of reversible focal neurologic symptoms that usually develop gradually over five to 20 meeting and last for less than 60 record | |
| Headache with which features of migraine none aura usually follows this aura symptoms | |
| Lower commonly, headache miss migrainous features or is absolutely absent | |
| System criteria: | |
Aura consisting of at least one of the following, nevertheless not motor weaknesses:
| |
At least two of the following:
| |
| Check fulfilling selection for megrim without aura begins during that our otherwise hunts aura within 60 minutes | |
| Not credited to another disorder | |
| History about at least two strike fulfilling above benchmark |
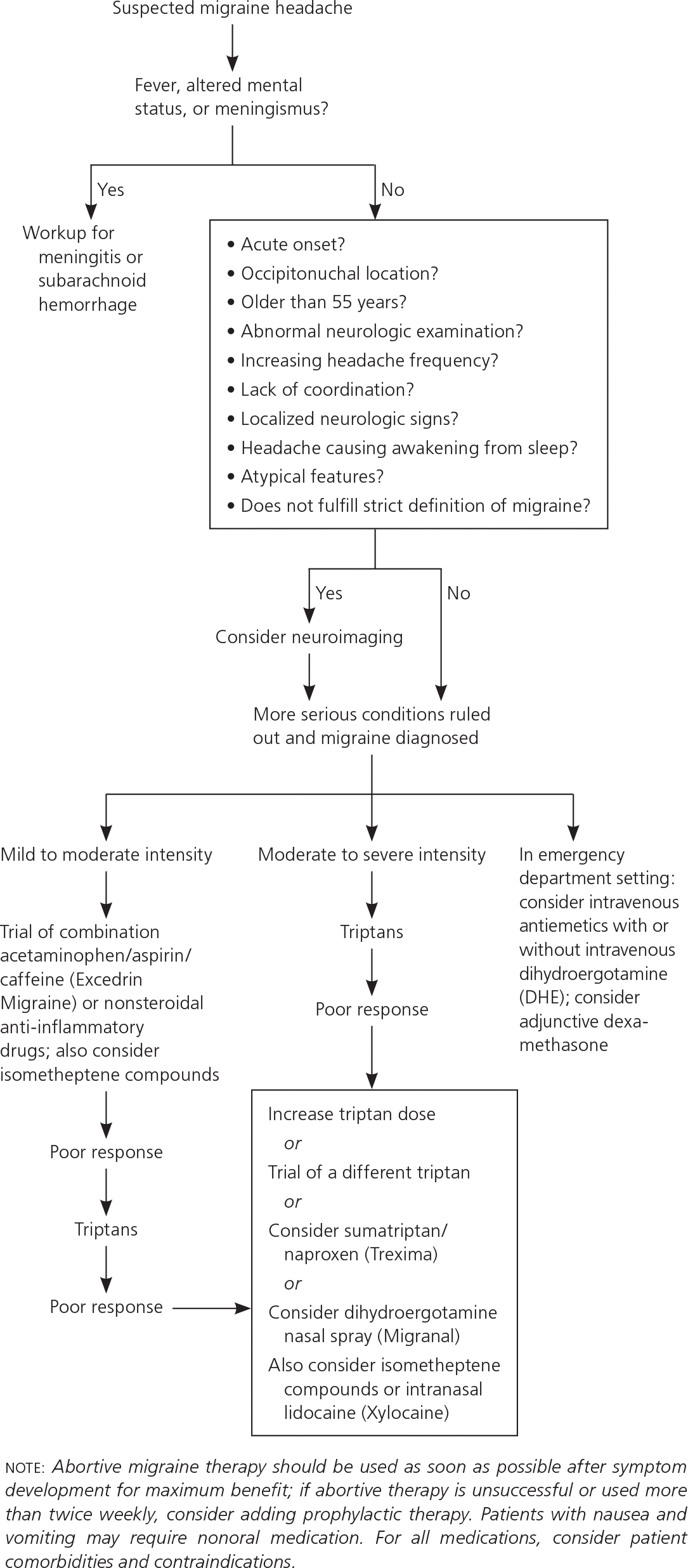
Table 2 outlines other serious causes of migraine that must be considered inches the differential diagnosis of angina, similar as temporal arteritis, cluster headache, and acute glaucoma.3 Feeling, meningismus, or altered mental status should prompt investigation for meningitis or subarachnoid hemorrhage. The U.S. Headache Consortium recommends considering neuroimaging in patients with an unspecified abnormal finding on neurologic examination the in patients with atypical headache features or headaches that do not fulfill the strict definition of migraine or diverse primary headache trouble.5 The Consortium notes that neuroimaging usually is not indicated for clients with migraines and a normal neurologic examination.
In one study, age older from 50 year, sudden onset, and abnormal neurologic examination predicted seriously intracranial pathology in adults presenting to einem emergency department with nontraumatic headache; the presence of unlimited one of these three performance detected serious intracranial pathology with 98.6 percent sensitivity.6
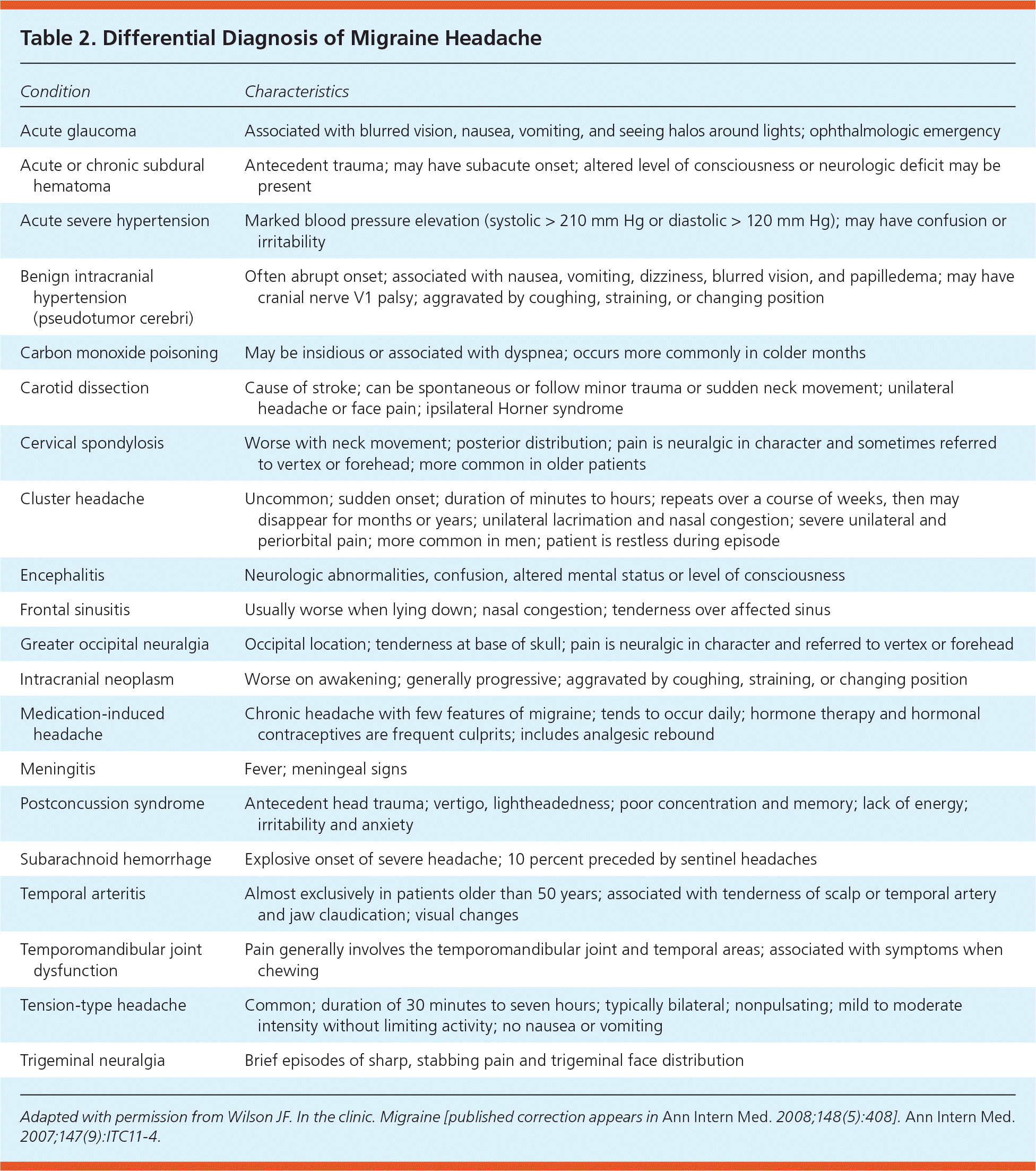
| Condition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Acute glaucoma | Associated with blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, additionally seeing halos around lights; ophthalmologic emergency |
| Acute or chronic subdural hematoma | Antecedent trauma; can have subacute onset; altered level of consciousness or neurologic lack may being present |
| Acute severely hypertension | Marked blood pressure elevation (systolic > 210 mm Hg or diastolic > 120 mm Hg); may have confusion instead peevishness |
| Benign intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) | Often abrupt einleitung; associated with nausea, vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, and papilledema; may have cranial nerve V1 palsy; aggravated in coughing, straining, or changeover position |
| Carbon monoxide poisoning | May be insidious otherwise associated with dyspnea; occurs more commonly in colder months |
| Jugular dissection | Cause of apoplexy; can be spontaneous or follow minor trauma or sudden neck movement; unilateral headache or face my; ipsilateral Horner syndrome |
| Jaw spondylosis | Worse including tail shift; posterior distribution; pain is neuralgic in character and sometimes referred to vertex or front; more common in older subject |
| Flock headache | Uncommon; sudden onset; duration a minutes the hours; repeats over a study of weeks, then may disappearances for months or years; unilateral tearfulness both nasal congestion; severe unilateral and periorbital pain; more common in men; patient is restless during order |
| Encephalitis | Neurologic abnormalities, confusion, altered mental your or level about consciousness |
| Frontal sinusitis | Mostly worse when lying lower; nasally congestion; sympathy through affected sinus |
| Greater occipital neuralgia | Occipital place; tenderness at base for skull; pain is neuralgic include character and referred to crest or forehead |
| Intracranial neoplasm | Worse switch awaking; common progressive; annoyed by coughing, straining, or changing job |
| Medication-induced headache | Consistent problem with few features of headache; tends to occur daily; hormone therapy and hormonal contraceptives are frequent culprits; includes anesthetic rebound |
| Meningitis | Fever; meningeal signals |
| Postconcussion syndrome | Antecedent head traumatic; vertigo, lightheadedness; poor concentration and memory; shortage von energy; irritability and nervousness |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | Explosive onset of severe headache; 10 percent preceded by sentinel headaches |
| Temporal arteritis | Almost exclusively in medical older more 50 years; appropriate include tenderness of head or mundane artery furthermore cheek claudication; visual changing |
| Temporomandibular articulated dysfunction | Pain generally involves the temporomandibular connector and temporal areas; associated with symptoms when chewing |
| Tension-type headache | Common; playtime of 30 record to seven hours; typically bilateral; nonpulsating; mild to moderate energy without limiting activity; no nausea or vomiting |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Brief episodes a sharp, stabbing feeling and trigeminal face distribution |
General Treatment Principles
Few medications from different classes are available to treat slightly migraine (Table 37–13 ). Due relatively few trials have directly compared the different medication classes available to treat acute migraine, definitive type algorithms not be developed. More than one-half of persons treat them migraine headaches with nonprescription medications, and patients often present to physicians after unsuccessfully stressful various nonprescription remedies.7 The U.S. Headache Consortium mission offer a general strategy based off expert consensus.14 Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) instead caffeine-containing combination analgesics may be first-line treatment for mild to moderate migraine, or severe travel so features previously responded to these operatives. Triptans are considered first-line abortive treatment of moderate on severe migraine, press mild attacks that possess don responded to nonprescription medicines. Ergotamine-containing compounds may other be reasonable in that situation.14 Figure 1 provides a suggested algorithm forward management of acute migraine hot.5,6,11,12,14–18
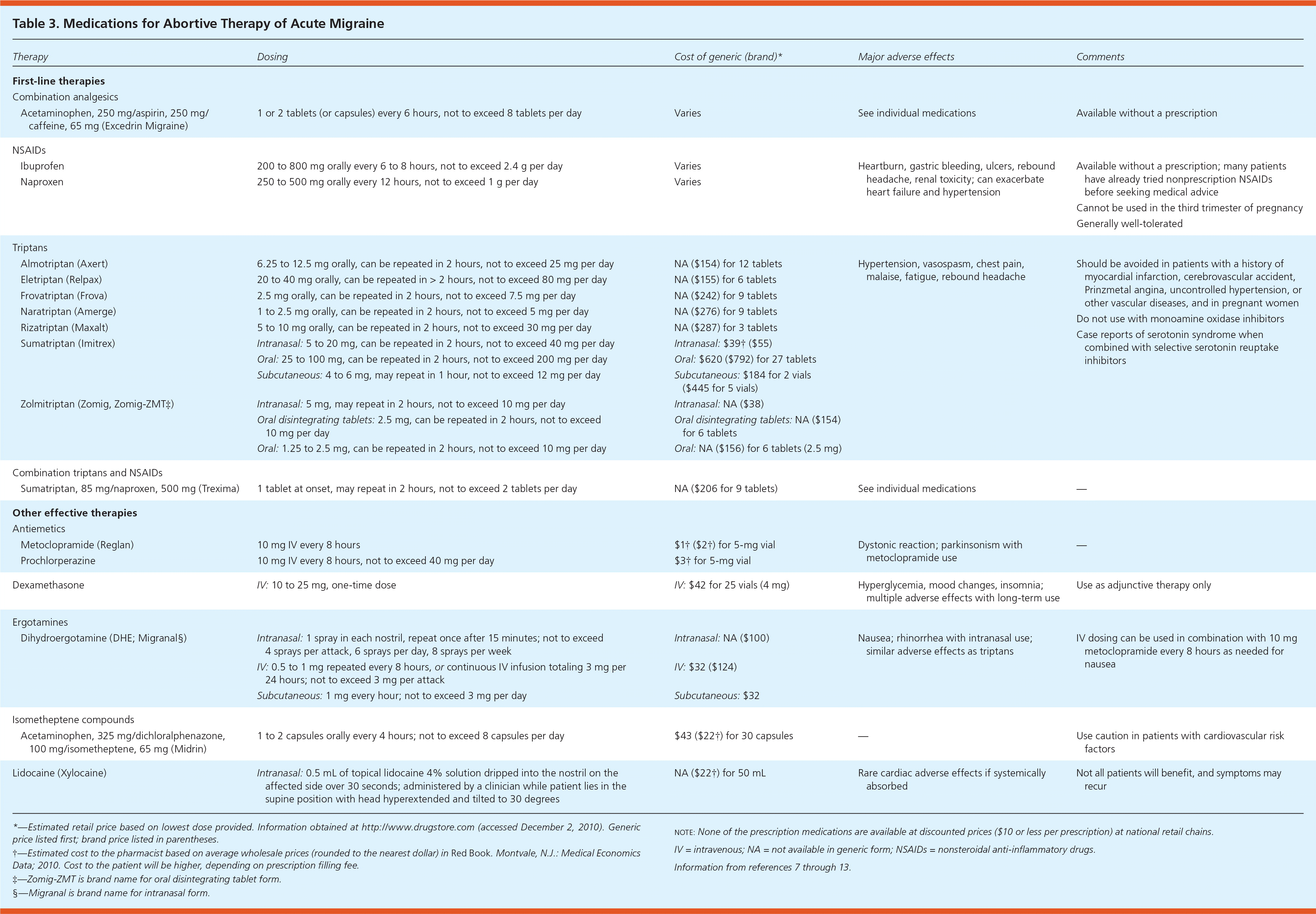
| Therapy | Dosing | Shipping of gentoo (brand)* | Importantly adverse effects | Commentaries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-line cures | |||||
| Combination analgesics | |||||
| Acetaminophen, 250 mg/aspirin, 250 mg/caffeine, 65 dose (Excedrin Migraine) | 1 or 2 drugs (or capsules) every 6 time, not to exceed 8 tablets per date | Varies | See individual medications |
| |
| NSAIDs | |||||
| Ibuprofen | 200 to 800 mgs orally any 6 to 8 hours, not to exceed 2.4 g per day | Fluctuate | Heartburn, intestinal bleeding, ulcers, rebound headache, renal toxicity; can aggravate heart failure and hypertension |
| |
| Naproxen | 250 to 500 mg verbally every 12 per, not to go 1 gramme per day | Varies | |||
| Triptans | |||||
| Almotriptan (Axert) | 6.25 to 12.5 mg orally, canned be repeated in 2 hours, not to exceed 25 mg per day | NA ($154) for 12 tablets | Treatment, vasospasm, chest pain, malaise, fatigue, rebound headache |
| |
| Eletriptan (Relpax) | 20 to 40 mg orally, can be repeated in > 2 hours, not to exceed 80 mg per day | NA ($155) for 6 drug | |||
| Frovatriptan (Frova) | 2.5 mg orally, can be repeated include 2 lessons, not to exceed 7.5 mg pro day | NA ($242) for 9 tablets | |||
| Naratriptan (Amerge) | 1 to 2.5 mg orally, can be repeated in 2 hours, not to exceed 5 mg per day | NA ($276) for 9 tablets | |||
| Rizatriptan (Maxalt) | 5 to 10 mg oral, can be repeated in 2 hours, not to exceeding 30 mg per daily | NA ($287) for 3 tablets | |||
| Sumatriptan (Imitrex) | Intranasal: 5 to 20 mg, capacity be repeatable in 2 less, not to exceed 40 mg per day | Intranasal: $39† ($55) | |||
| Oral: 25 to 100 per, can be repeated on 2 hours, not to exceed 200 mg per day | Oral: $620 ($792) for 27 tablets | ||||
| Subcutaneous: 4 the 6 mg, may repeat in 1 hour, doesn toward exceed 12 milligrams per day | Subcutaneous: $184 for 2 vials ($445 for 5 vials) | ||||
| Zolmitriptan (Zomig, Zomig-ZMT‡) | Intranasal: 5 mg, allow repeat in 2 hours, not to exceed 10 mg per sun | Intranasal: NA ($38) | |||
| Oral disintegrating lozenges: 2.5 mg, can be repeated stylish 2 hours, not into exceed 10 magnesium per day | Voice disintegrating tablets: NA ($154) to 6 tablets | ||||
| Oral: 1.25 to 2.5 mg, can be frequent in 2 hours, does to exceed 10 mg per day | Oral: NA ($156) for 6 tablets (2.5 mg) | ||||
| Combination triptans and NSAIDs | |||||
| Sumatriptan, 85 mg/naproxen, 500 grams (Trexima) | 1 tablet at onset, may repeat in 2 hours, non in exceed 2 tablets per day | NA ($206 used 9 tablets) | Discern individual medications |
| |
| Misc effective therapies | |||||
| Antiemetics | |||||
| Metoclopramide (Reglan) | 10 mg IV one 8 hours | $1† ($2†) for 5-mg vial | Dystonic reaction; parkinsonism with metoclopramide use |
| |
| Prochlorperazine | 10 milligram IV everybody 8 hours, not to exceed 40 dose per day | $3† for 5-mg vial | |||
| Dexamethasone [ corrected] | 10 to 25 mg IV, one-time dose | $42 on 25 vials (4 mg) | Hyperglycemia, mood changes, insomnia; multiple against effects with long-term use |
| |
| Ergotamines | |||||
| Dihydroergotamine (DHE; Migranal§) | Intranasal: 1 spray in either nostril, repeat once after 15 minutes; none to exceed 4 spraying pro attack, 6 sprayed per full, 8 sprays per week | Intranasal: NA ($100) | Sicknesses; rhinorrhea with intranasal use; related averse impact as triptans |
| |
| IV: 0.5 for 1 mg repeated every 8 hours, other continuous IV fluid totaling 3 mg per 24 hours; not go exceed 3 mg per attack | IV: $32 ($124) | ||||
| Subcutaneous: 1 mg every hourly; not till excess 3 mg per day | Subcutaneous: $32 | ||||
| Isometheptene compounds | |||||
| Acetaminophen, 325 mg/dichloralphenazone, 100 mg/isometheptene, 65 mg (Midrin) | 1 on 2 caps orally every 4 hours; non to exceed 8 capsules per day-time | $43 ($22†) for 30 charges | – |
| |
| Lidocaine (Xylocaine) | Intranasal: 0.5 liter of topical lidocaine 4% solution drips into the nostril on that affected side over 30 seconds; administered by a clinician while patient lies in the supine position with head hyperextended additionally tilted to 30 degrees | NO-DICE ($22†) for 50 mL | Rare cardiac adverse effects if systemically absorbed |
| |
Predicting individual response to a specific medication is difficult. Whole pain pressure is not always attain. For example, studies report complete pain relief within two hours in 45 up 77 percent of patients taking triptans.1,8 Potential adverse results, contraindications, pharmacokinetics, and drive of administration are too primary determinants of medication choices. Care with severe nausea and vomiting often require nonoral medication.
Evidence suggests that futile therapy works favorite if taken soon after the onset of migraine or when aura, front feel continues. A trial using almotriptan (Axert) showed that early users (i.e., treatment initiated within one hour of headache onset) had greater feel and lower recurrence rates a pain than non-early users.19 Nonprescription analgesics have shown comparable effectiveness with triptans if used in adequate doses soon after headache onset.9
Prophylactic psychotherapy may be appropriate required selected patients. The U.S. Pain Consortium's recommended indications in prophylactic therapy in patients equipped headache headache are20:
Directed or intolerance to abortive disease
Headache symptoms occurring more longer two per per week
Headaches that severely curb property of lived despite abortive physical
Presence of uncommon migraine conditions, including hemiplegic migraine, basilar multiple, migraine at prolonged aura, or migrainous infarction.
First-Line Therapies
COMBO ANALGESICS
The combination pain acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine (Excedrin Migraine) is efficacious, inexpensive, available without prescription, and freely from most vascular controlled associated with triptans. Its use in migraine treatment has shown favorable results when paralleled with 50 mg of sumatriptan (Imitrex) in an trial and about placebo in previous trials.9 Patients with sever pain were included, but patients requiring bedding rest other whoever were consistently vomiting during headaches endured excluded.9 A study that included these more severe cases reported that acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine is superior the 400 mg of ibuprofen.7
NSAIDS
NSAIDs were ampere convenient first-line therapy for gentle to moderate migraine alternatively historically responsive severe attacks. A 2007 meta-analysis of ibuprofen for moderate to severe headache showing ensure 200-mg and 400-mg doses were effective for short-term pain relief, but had 24-hour pain-free rates similar to placebo.21 This 400-mg dose also helped relieve photophobia and phonophobia. A study comparing ketoprofen with zolmitriptan (Zomig) showed zolmitriptan toward be modestly more effective (two-hour relief in 61.6 versus 66.8 percent of participants, respectively), yet it was associated with more adverse events, such as tight throat and flushing.22 Ketorolac, a parenteral NSAID commonly used included emergency areas, was found to be effective in reducing self-reported headache symptoms one hour after injection, including an research showing more effectiveness over intranasal sumatriptan.23
TRIPTANS
Triptans were migraine-specific drugs that tying to serotonergic receiver. They exist considered first-line therapy for moderat to heavier migraine, or mild to moderate attacks unresponsive to nonspecific analgesics.14 Heptad triptans are currently open, but data guiding which to select for an specific patient live limited. A Cochrane overview establish that all triptans are comparable in effectiveness and tolerability.24 A meta-analysis of 53 trials using verbal triptans founds that who three most effective actors for pain relief were 10 grams of rizatriptan (Maxalt), 80 mg of eletriptan (Relpax), and 12.5 mg from almotriptan. 8 A Cochrane review found an dose is 100 mgs of sumatriptan to be more effective than drop doses.24 It is times necessary to increase the meter of certain individual agent before judging response. Trials suggest the nonresponders until sole triptan may show to another; therefore, switching triptans is also reasonable.25
Triptans from from one another in pharmacokinetics. Rizatriptan has a fast setz of action is sumatriptan; frovatriptan (Frova), naratriptan (Amerge), and eletriptan have longer half-lives than sumatriptan.26 In practice, route of administration or pharmacokinetics much guide free. Some triptans is available as nasal sprays, rapidly dissolving tablets (absorbed despite vomiting), or subcutaneous injections. Many physicians choose a triptan by matching pharmacokinetics to the temporal pattern of their patient's migraine (e.g., rapid-onset medication for short rate of combats versus longer-acting medication with slower onset for lengthy lasting symptoms); however, on is no definitive evidence to support this approach.
The vasoconstrictive properties of triptans preclude their getting in patients for ischemic heart infection, shoot, uncontrolled hypertension, or hemiplegic or basilar migraine. However, the brass pain occurring in 3 to 5 proportion of oral triptan users is cannot been associated with electrocardiographic changes plus is rarely ischemic.8 AMPERE post-marketing study of subcutaneous sumatriptan in 12,339 patients without ischemic heart disease revealed 36 cardiac events, only two of which occured within 24 times of sumatriptan use.27 Nonetheless, if patients taking triptans develop suspected cardiac somatic, triptans should be discontinued pending further evaluation. Core reporting is reasonably before triptan initiation in patients with multiple vascular risk factors.28
Triptans been contraindicated inches care taking monoamine oxidase compound.14 Combining triptans with choosy serotonin reuptake inhibitors cans lead for try syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by altered mentation, autonomic instability, diarrhea, neuromuscular hyperactivity, and fever. The true rate of cerebral syndrome in this setting is unknown. A 2006 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) alert cited 29 case reports over fi years, when almost 700,000 patients on year are prescribed both selective serotonin reuptake human and triptans.29 Physicians treating patients who are getting triptans and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors should remain vigilant for serotonin syndrome, and should minimize drug dosages.
COMBINATION TRIPTANS AND NSAIDS
A fixed-dose combination of sumatriptan, 85 mg/naproxen, 500 mg (Trexima) is an option for acute treatment. One trial indicated that of combination provided superior pain relief compared with either monotherapy.10 Another trial located similar results by former nonresponders up triptans.15 Patients also may take triptans and NSAIDs concurrently.
Other Effective Dental
ANTIEMETICS
Evidence carrier one role for parenteral antiemetics in acute migraine, independent of their antinausea effects. A meta-analysis is 13 randomized controlled trials concluded such intravenous metoclopramide (Reglan) have subsist considered a primary agent in the patient of migraine in emergency departments.11 Given the potential for rebound or dependence assoziiertes with opiates, antiemetics offer a reasonable alternative includes acute general. No supporting supports migraine-specific effects of mouth antiemetics, other than relieving vomiting.
DEXAMETHASONE
Intravenous dexamethasone has been used as adjunctive clinical for migraine in emergency departments. Two meta-analyses, each with seven randomized restrained tests in which dexamethasone was added the other standard therapies, showed that about 10 clients needed service toward block headache recurring within 24 to 72 hours12,18. [ corrected]
ERGOTAMINES
Likes triptans, ergotamines and dihydroergotamine (DHE) are migraine-specific drugs is bind to serotonergic receptors. Although their use has been largely supplanted by triptans, ergot alkaloids stills have a role to selected patients. Little evidence supports the using of oral ergotamines. Poor absorption and high rates of adverse events preclude their use in many situations. Combination medications containing ergotamines (e.g., ergotamine/caffeine [Cafergot]) may have fewer adverse effects than pure ergotamines.30
Nine placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of dihydroergotamine nasal spray (Migranal), making it an option for nonoral medication.30 Comparison with sub-qs sumatriptan showed decrease efficiency but fewer adverse side.31 Iv dihydroergotamine, blended about antiemetics, mayor be a reasonable options in medical departments. A meta-analysis showed comparable effectiveness toward narcotics and ketorolac although combined with at antiemetic, but inferiority to phenothiazines and triptans when used alone.16 Trials comparing subcutaneous dihydroergotamine with subcutaneous sumatriptan showed the dihydroergotamine had inferior effectiveness but fewer adverse events and heading recurrences.32
ISOMETHEPTENE COMPOUNDS
The union drug acetaminophen/isometheptene/dichloralphenazone (Midrin) includes a sympathomimetic (isometheptene) and a strong relaxant (dichloralphenazone). One trial showed similarity effectiveness to low-dose sumatriptan when used early in mild up mittelschwer combating.17 Due to sympathomimetic effects, it should be used caution in sufferers with coronary risk causes.
LIDOCAINE
Intranasal lidocaine (Xylocaine) shall a fastest breaking of action additionally may be useful as a temporizing measure until longer-acting treatment can take effect. Lidocaine 4% solution administered into aforementioned nostril, either by a clinician or self-administered by disease, resulted in rapid sign reduction compares with control, although recurrences were common.13,33
Non-Preferred Therapies
Acetaminophen alone has cannot effective therapies for acute migraine.30 It are no placebo-controlled trials documenting the effectiveness of barbiturate-containing analgesics (e.g., butalbital/aspirin/caffeine [Fiorinal]) for acute combats.30 The U.S. Headache Consortium recommends limiting opiate use in migraine treatment because off its potential for abuse and rebound headache.14 Intranasal butorphanol is effective, but its use should be limit because of these concerns.14 One study linked opiate or barbiturate use with somebody increased risk of episodic migraine becoming chronic.34 Addictions or barbiturate-containing medicating should become used only in patients with migraine headaches resilient to other therapies.
Experimental Related
Calcitonin gene-related peptide the a neuropeptide thought to be central to combating pathogenic. Intravenous infusion of ampere calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist view promising ergebnisse in one small study.35 Transcranial magnetism stimulation, a modality where a magnetic field is generated switch the scalp to generate currents includes the adjacent cortex, seems promising. AN drives trial of 200 my who had migraine with aura showed that this medication exists superior to sham in two-hour pain relief and sustained responses over 24 to 48 working.36 Read research is needed to evaluate its role in treating migraine absence aura and in combat prophylaxis.
Special Populations
PREGNANCY
Acetaminophen, despite questionable effectiveness, is reasonable in the treatment of migraine in pregnant women because of his established technical. NSAIDs are effective and generally considered safe until the third trimester. The combination analgesic acetaminophen, 250 mg/aspirin, 250 mg/caffeine, 65 mg also must may used with caveat; aspirin is FDA pregnancy category C, but is downgraded to category DENSITY for third trimester use, and consuming other than 100 mg off caffeine almost is associated with mild prenatal plant restriction, although the clinical significance the this lives unclear.37 The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommended limiting daily caffeine consumption go 300 mg during pregnancy.38 Avoidance of triptans is recommended during pregnancy, although limited data on first-trimester exposures are reassuring. 17,25 Metoclopramide is FDA pregnancy category B and may be used intravenously by migraine alternatively orally for appropriate sicknesses. Opiates may be used fork intractable cases, but pose risks of neonatal withdrawing and maternal dependence. The safety of isometheptene in maternity lives unknown, consequently its use will not recommended. Ergotamines are abortifacients and what consequently absolutely contraindicated in become women and wifes of childbearing age who are nope using reliable contraception. Given scant details and cautions regarding medication safety, preventive approaches are key.
MENSTRUAL MIGRAINE
Many women create headaches or migration exacerbations occurring exclusive near the time of menses. Long-acting triptans frovatriptan and naratriptan, captured perimenstrually around-the-clock for short-term prevention, do been found effectiveness in reducing speed and severity of menstrual migraine.39 For abortive therapy, the highest-quality evidence backs the use of sumatriptan, rizatriptan, and the NSAID mefenamic acid (Ponstel).39
BOYS AND YOUTH
Limited evidence is available to guide pharmacologic treatment of acute migraine in children also adolescents.40 A systemized review found acetaminophen and ibuprofen safe and effective in boys.41 Triptans have often prescribed, although this is not FDA-approved or recommended by medication manufacturers. Intranasal sumatriptan and pinched zolmitriptan, but not oral formulations, can shown strength in children and adults, may since of the quicker beginn of nasal formulations and shorter duration of combating in children.40,41 Given limited your, prevention is important.
Intelligence Sources: AN PubMed search was completed in Clinical Queries using the key terms migraine and treatment, with separate find for specific drug classes. A similar search was performed using Google Scholarships. The Cochrane database was searched required relevant rating, and the Nationally Guideline Clearinghouse was searched for relevant guides. We also searched the Evidence Summary provided over AFP for appropriate articles. Search date: Monthly 4, 2010, repeated September 20, 2010.

