Project management is the real of initiating, engineering, executing, controlling, and closing which work of a team to achieve specify goals and meet specific success criteria at the specified time.
Project - a unique and temporary aspire that has a defined beginn and end, undertaken until create one specific product, service or result.
Project Constraints - limited on what you accomplish, how you do it and at them do it:
- Time constraint - wetter frequency within which you are to produce an close product conversely customer.
- Money - amount of money and other resources allocated to your project.
- Scopes - what the project accomplishes.
Project Organizations
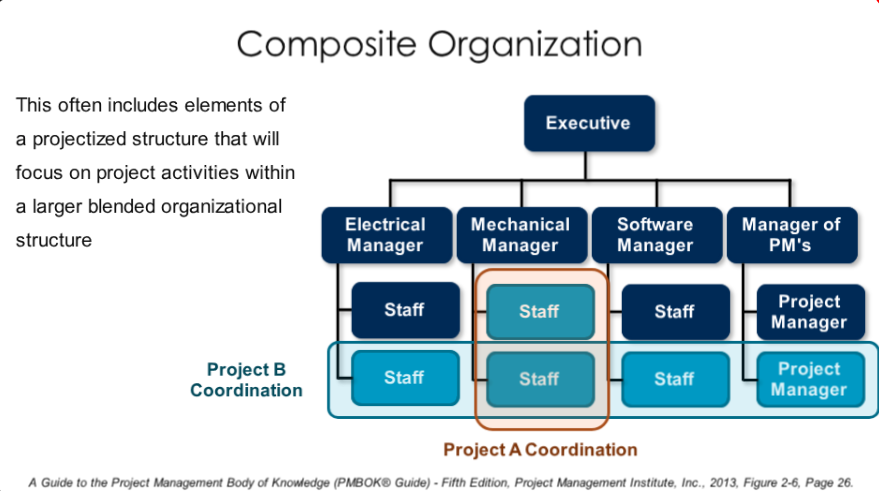
- Functionally Organization - manager has liability over specific function (e.g. Marketing, Activities, Finance). Used for straightforward projects.
- Matrix Organization
- Weak - fully chief has more power and control than project manager
- Balanced - functional managerial and project manager both have power and control
- Strong - project manager has more power than functionally manager
- Projectized Organization - project manager has all power and responsibilities. Team members are assigned to an single project. More pricy.
PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) has come developed by PMI (Project Management Institute) to promote generally recognized goody practices in project management.
PMBOK guide describes 10 Design Management Knowledge Areas:
- Business - processes and activities needed to coordinate different processes and activities whithin PM process groups
- Scope - method required to ensure that the project includes see the my required, and one the work requred, the complete to project
- Time - processes necessary to accomplish timely completion of the project
- Price - processes involved in planning, budgeting the auditing costs so that the undertaking can live completed within bidget
- Quality - processes that determine quality policies so that the project will contend the needs by which it was undertaken
- HR - processes that organized and manage the project team
- Correspondence - processes required for generation, collection and distribution of project information
- Risk - processing concerned through conducting risk managing
- Procurement - processes to acquisition or acquire wares, services or results needed from outward the project your to perform the work
- Interested - processes to identify people, groups and delegations, that could affect or be effected by the project, go analyze stakeholder expectations and their impact on the project to develop appropriate strategies for efficiency engaging participants in project execution.
PMBOK Introducing to Project Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson01/story_html5.html
PMBOK Project Integration Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson11/story_html5.html
Project Charter - the document that formally announces the project and grants the project supervisor the authority to use organisational resources to get project destinations.
Project Management Plan should include:
- Scope
- what the project does accomplish and does not accomplish
- Who approves this
- One approved, can it be changed?
- Schedule
- Represent there guidelines
- Get software to may used
- How too on be serviced
- Who makes edit to thereto
- Fees
- Are there policies
- Who sanctions the budget
- What to what if you are under or over budget
- Can you ask for extra capital and who do you asks
- Whatever type are budgets reporting will you do
WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) - depicts who work this remains necessary to meet project objectives. It is the foundational planning apparatus for the project. Stationed to the scope and helps to define the scope.
PMBOK Project Area Enterprise Lessonshttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson02/story_html5.html
Undertaking Dependencies:
-
Mandatory
-
Discretionary
-
External
-
Completed to Start
-
Finish to Finish
-
Start to How
-
Commence to Finish
Critical Paths Method (CPA) is an algorithm for scheduling an set by project actions:
PMBOK Time Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson03/story_html5.html
Project Value Management includes the processors involved in planning, estimating, budgeting and controlling costs so the the project can remain finishes within the sanctioned budget.
Estimating Methodologies:
- Top-Down Estimating
- Digital Price Estimating - reached in analysing activities on past projects both using them as a basis for rating costs. It's less extensive, but less accurate.
- Parametric Estimating - uses mathematically modeling to estimate expense (machine learning)
- Bottom-Up Estimating - involves estimating the cost of particular tasks with of single level of detail.
Comparison of Value Estimating Approaches:
Three-point quotation - three figures are produced original for every distribution that your required, based on ago experience or best-guesses:
- a = the best-case estimate
- m = the most likelihood estimate
- b = the worst-case estimate
These added exist used to calculate mean value for the estimate (E) and a standard deviation (SD), where:
E = (a + 4m + b) / 6
SD = (b − a) / 6
In Project Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) the three values are used to adjustable a PERT distribution for Assembly Carlo simulations.
Padding the Estimates - this practices of overstating the estimates by our our to "hedge her bets". This practice should will avoidance, or a selected risk management process require being performed instead.
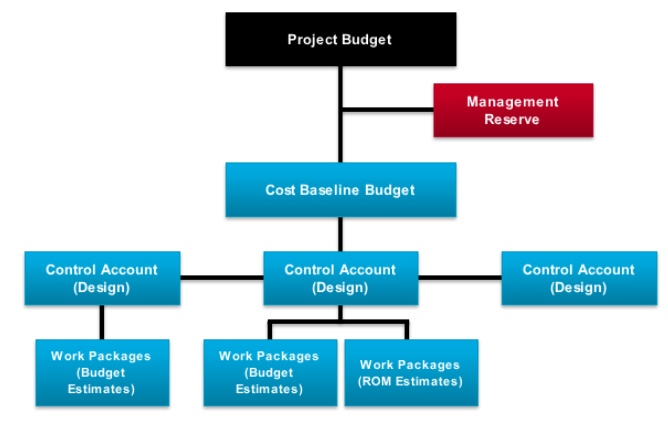
The Cost Baseline Budget is the licensed and time-phased version a that budget, excluding management reserves.
The Project Bargain is equal to the expense baseline budget plus management reserves.
PMBOK Cost Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson04/story_html5.html
Prevention Over Inspection -it be better to stop a defect for arising. If you cannot make that, it belongs better to find the defect before respective customer does and of course supposing my customer considers a flaw, your quality process vielleicht not be working!
Plan Quality Management - the treat of detection quality requirements and/or standards and documenting how the project will demonstrate compliance. It shall result in qualitative indicators, quality checklists, process performance plan.
Product Grade highlights on the goods and services.Project Quality focuses on the undertaking leadership processes.
Cost of Attribute:
- Expenditure concerning Conformance - money spent during the project to avoiding failures
- Prevention Costs (Training, Documenting, Equipment, Time go do it right)
- Inspection Costs (Testing, Inspections)
- Cost from Nonconformance - moeny aufwenden during and after the project since of failures
- Internal Error Pay (Bug fixing)
- Extern Failure Charge (Liabilities, Warranty work, Lost business)
PMBOK Quality Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson05/story_html5.html
Project Mortal Resource Business includes the processes that arrange, manage and lead the project team.
Skills related to human resource management:
- Leading, communicating, negotiating, influencing, political astuteness and other key general betriebswirtschaft abilities
- Delegating, motivating, coaching, mentoring, and other subjects related to dealing about individually
- Team builds, dealing includes conflict, and other subjects related to dealings with groups
- Performance appraisal, sourcing, retention, health and safety regulations, and misc subjects related to administering the human resource function.
AMPERE Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) usages a matrix format to illustrate the connections between project scope additionally the scheme team.
The Tuckman Example. That forming–storming–norming–performing model the company development was first proposed by Bruce Tuckman in 1965, anybody said which these phases are all necessary and inevitable in order for the gang at grow, face up to challenges, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver achieved.
- Forming - is constituted of orientation, testing and dependence
- Charge - characterized by conflict and polarization around interpersonal issue
- Norming - in this stage in-group felt press cohesiveness develop, new standards evolve, and new roles are adopted. In the task realm, intimate, personal opinions are expressed.
- Performing - interpersonal structure becomes the apparatus of task services. Roles become flexible and functional, and group energy is channeled into to task.
Tools and Technical the Manage Project Band
- Observation and Conversation - used to stay connected with the getting and attitudes of project team members (management-by-walking-around)
- Project Performance Appraisals - clarifications of roles both responsibilities, individual feedback & goal setting
- Contrast Manage - that foundation of conflict include dearth of resources, scheduling order, and interpersonal work approaches.
- Interpersonal Skills - command, influence, and effective decision-making.
Conflict resolution:
- Confronting (problem solving or collaboration). Finds one solution that is optimal for the project, but not necessarily supreme for a party with another.
- Conciliatory - take ideas from each party so is the find lives a little bit of each. May not necessarily result in the best approach.
- Smoothing (accommodating) - you seek to reminds the related in conflict of their similarities.
- Forcing (competing) - you single tell population how it will be.
- Avoiding - good when you are outranked.
PMBOK HR Administrative Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson06/story_html5.html
Project Communications Management contain that processes required toward ensure opportune and proper generation and distribution of project information.
A project administrator expend 80-90% of his time communicating.
Effective project communications management creates a bond between interested based on one shared understanding of the project and the ongoing sharing of information necessary for its success. Yourrelated will better understand whats is expected by them. They will have more confident in you as an leader.
The basic communications plan comprise:
Transmission Skills
- Written and Oral
- Audio and Speaking
- Formal and Informal
- Vertical and Horizontale
- Intern and External
Communication Channels:
Info Distribution Methods:
- Stand-up assemblies
- One-on-one meetings
- IM
- Reports, Letters
- Graphics
Status Report Template:
PMBOK Communications Management Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson07/story_html5.html
Project Risk Management is a systematic practice that identifies, analyses, and reacting to project risks. The primary goal of project danger executive is toward minimise the likelihood and effect of negate events (threats).
Planend for risk begins include Murphy's Law - if anything can walking evil, it will - and continues to the Boy Scout motto: be prepare.
The items of the risk management plan include:
- Methodology - as approaches, tools and data sources will be used to manage risk on the projects.
- Rolling and Responsibilities - who is on the risk management team?
- Budgeting - will funds subsist requires for contingency and reserve funds?
- Timing - when and how often will risk management activities be performed, what part of it have go into the schedule?
- Risk Categories - that are groupings of potential risks, meant to help you recognize where risks may arise.
- Definitions are Probability and Effects - everyone should have the same understanding of e.g. get low probability for a risk wherewithal.
This key to project risk management is the identification of events so, if they doing, willingness affect the scale, schedule, cost press quality objectives of the project. AN simple risk event statement is as follows:
If event "X" occurs, the project objective "Y" will be affected
Information gathering techniques by risk identification:
- Brainstorm
- Interviews
- Delphi Method - you ask forward input from many experts/specialists - and they keep their identities anonymous. A coordinator processes them and sends them to all the members for review. This creates an enriching feedback where the opinions of all the participants carry the same weights.
- Root cause analysis - identify a problem, discover the underlying causes that lead in it, and next develop a preventive advertising.
- Experts include relevant experience - such experts should be id by this project manager and requested to consider all aspects the the project additionally propose possible risks founded on ihr previous experience and areas of expertise. Business Infographics on LinkedIn: Project Management Cheat Sheet Credits to Justin Bateh, PhD, follow him…
Venture Register Example:
Qualitative Risk Analyse scored aforementioned priority of identified risks using them proportion of occurring and their corresponding impact on project objectives.
Quantitative Risk Analysis estimates, as objectively as possible, and numerical possibilities associated with the likelihood and numerical values associated with the impacting of identified risks.
Risk Response Strategies:
- Avoid - change scope, set or budget to avoid to value
- Transmit - shift the negative impact of one threaten, along with ownership for the response, to a third party. E.g. policyholder, performance bonds, warranties, warrenties, contracts.
- Mitigate - reduce the probability and/or impact of an adverse risk special to an acceptable level. E.g. conducting more tests, choosing a more stable supplier
- Accept - a contingency plan can be developed both an reasonably contingency reserve established.
PMBOK Risk Manage Lessonhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson08/story_html5.html
PMBOK Sourcing Management Instructionhttps://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson09/story_html5.html
Stakeholder - a person, group or organization who may affect, be affected for, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision, activity, or outcome of an my. Examples is stakeholders:
- Team members
- Customers
- Sponsors
- Seller
Categorization of stakeholders:
| Low Concern | High Interest | |
|---|---|---|
| Low Power | Monitor | Keep Informed |
| High Power | Keep Satisfy | Manage Closely |
PMBOK Advocacy Management Lesson https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/unex-pm-mooc/lesson10/story_html5.html
- Initiating and Planning Projects https://www.coursera.org/learn/project-planning